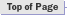Before The Public Utilities Commission Of The State Of California
Order Instituting Rulemaking on the Commission's own Motion Into Competition for Local Exchange Service. |
R.95-04-043 (Filed April 26, 1995) |
|
Order Instituting Investigation on the Commission's own Motion Into Competition for Local Exchange Service. |
I.95-04-044 (Filed April 26, 1995)
|
REPORT ON THE 858 AREA CODE
Submitted in Compliance with California Public Utilities
Code Section 7937, CPUC decision 99-12-051, and Administrative Law Judge
Ruling Issued On January 18, 2000
CALIFORNIA PUBLIC UTILITIES COMMISSION
TELECOMMUNICATIONS DIVISION
Respectfully submitted
October 10, 2001
Jack Leutza, Director
Telecommunications Division
505 Van Ness Avenue, 3rd Floor
San Francisco, CA 94102
REPORT ON THE 858 AREA CODE
CALIFORNIA PUBLIC UTILITIES COMMISSION
TELECOMMUNICATIONS DIVISION
October 10, 2001
Prepared by Telecommunications Division:
Michael Amato John Miller
Robert Benjamin Michaela Pangilinan
Mary Jo Borak Craig Stevens
Cherrie Conner Karen Watts-Zagha
Jack Leutza Sue Wong
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 1
BACKGROUND 2
FINDINGS 3
CHAPTER ONE: OVERVIEW OF NUMBERING 6
A. Inefficient Use and Increasing Demand for New Numbers in California Is Causing Area Code Proliferation 6
B. 858 History and CPUC Decisions 7
1. Code Administration Allocates Prefixes 8
C. CPUC Efforts to Resolve Area Code Proliferation 9
1. Number Pooling 9
2. Improved Number Inventory Management 11
3. CPUC Efforts at Federal Level 12
4. Utilization Studies 15
CHAPTER TWO: 6.0 MILLION UNUSED NUMBERS IN THE 858 AREA CODE 16
A. The Scope of the Utilization Study 16
1. Distribution Statistics of Prefixes 16
2. Companies Reporting 17
3. Non-Reporting Companies 17
B. 6.0 Million Numbers Available in the 858 Area Code 17
C. Analysis of Available Numbers 21
1. Analysis of Wireline Carriers' Contamination Rates 21
2. Analysis of Wireless Carriers' Contamination Rates 22
3. Potential Block Contamination Abuses 24
4. Reclamation of Prefixes 25
D. Analysis of 1.7 Million Unavailable Numbers 26
1. 1.4 Million Assigned Numbers 27
2. Reserved Numbers Are a Potential Source of Additional Numbers 31
3. Restrictions on Administrative Numbers Could Yield More Numbers 33
4. Intermediate Numbers 34
5. Aging Numbers 36
6. The Need to Audit the Data 37
CHAPTER THREE: NUMBER POOLING AND OTHER NUMBER CONSERVATION MEASURES 39
A. Introduction 39
B. Number Pooling 39
1. More Accurate Forecasting Will Improve Number Pooling 40
C. Lack of Local Number Portability Stands a Key Barrier to Pooling 41
D. Unassigned Number Porting 42
E. Consolidation of Rate Centers to Maximize Number Use 44
F. Sharing Prefixes May Yield More Efficient Number Use 46
CONCLUSION 48
Appendix A
Appendix B
Appendix C
Appendix D
Appendix E
Appendix F
Appendix G
Appendix H
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Like much of the country, California currently is experiencing a numbering crisis. From 1947 to January 1997, the number of area codes in this state increased gradually from 3 to 13. During the next three years, however, the number of area codes in California nearly doubled. By the end of 1999, California had 25 area codes statewide. The California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) recently implemented several measures intended to ensure efficient use of telephone numbers. Without the implementation of major number conservation measures, the telecommunications industry had plans underway to add 22 more area codes in California by the end of 2003, resulting in a statewide total of 47 area codes.
This study recounts the history of the 858 area code, from the time it was included in the 619 area code. It now covers the northern part of San Diego in Southern California. This report should be viewed in a broader context than the facts pertaining solely to the 858 area code. The report evaluates the status of number availability in the 858 area code, and discusses the various state and federal policies which govern number use in California and nationwide. In addition, the report analyzes number use by carrier category and identifies what measures the CPUC can employ in the 858 and other area codes to improve efficiency of number use in order to prematurely avoid opening new area codes. Data is self-reported by the companies; the CPUC staff has not audited any 858 utilization data submitted for this study and report.
The utilization study sheds new light on the numbering crisis in the 858 area code. The data reveals that despite increasing demand for numbers, the 858 area code is not fully utilized. The study found that of the 7.7 million useable numbers in the 858 area code, 6.0 million, or approximately three quarters are presently not in use. The data further establishes that the 858 area code possesses considerable room for growth, and thus, aggressive measures such as splits or overlays are not yet warranted in the 858 area code. The report further urges the CPUC to seek from the FCC authority to implement Unassigned Number Porting (UNP) as a means to more efficiently use numbers still available in the 858 area code.
This report is filed in compliance with CPUC Decision (D.) 99-12-051, and with AB 406, enacted by the California Legislature in the 1999 legislative session. (Chapter 99-809, 1999.) AB 406, codified as Public Utilities Code Section 7937, requires the CPUC to obtain historical telephone number use data from every telecommunications company in California. The CPUC's Telecommunications Division (TD) first obtained and analyzed data from the 310 area code in Los Angeles late in 1999, and produced a utilization report on 310 in March 2000. In November 2000, TD completed utilization reports covering the 415, 510, 818, and 909 area codes. TD also released utilization reports on the 408, 619, 650, and 714 area codes in March 2001. In May 2001, TD released another four reports covering the 323, 562, 916 and 925 area codes. In July 2001, TD released an additional four reports on the 626, 707, 805, and 949 area codes. This report on the 858 area code continues TD's analysis covering specific area code number utilization levels.
BACKGROUND
The 858 area code contains approximately 7.7 million telephone numbers. These numbers are available to telecommunications companies that obtain the numbers from the North American Numbering Plan Administrator (NANPA),1 and in turn, assign the numbers to their customers for their immediate use. Alternatively, companies may reserve numbers for future use, or retain numbers for some internal (administrative) use. Some companies provide blocks of numbers to resellers or "dealers", which then assign those numbers to customers. The FCC deems numbers that companies allocate to resellers to be "intermediate" numbers. In addition, each assigned number, after disconnection, must "age" during a transition period before assignment to the next customer. Many companies have inventories of numbers in the "aging" process. Finally, some numbers in this area code are not available for public use, as they have been set-aside for emergency purposes, for technical network support, or for other reasons. The FCC has determined that numbers in these five categories - assigned, administrative, reserved, intermediate, or aging - are unavailable, either because they are already in use or are designated for some present or future use.
FINDINGS
TD's analysis shows that of the 7.7 million available numbers, 2.7 million are available for allocation for companies seeking numbers and 1.3 million have been set aside for donation to the future 858 number pool.2 Companies possess the remaining 2.0 million unused numbers. Wireline carriers, such as Pacific Bell and many competitive local exchange carriers, hold roughly 1.6 million available numbers, while wireless carriers and Type 1 carriers hold approximately 399,000 available numbers.
At the same time, the 858 study finds that under FCC rules, about 1.2 million of the numbers held by companies cannot be allocated to other companies, nor can they be contributed to the future 858 number "pool" for reassignment to other companies. The FCC has determined that wireless carriers do not have to participate in the pool at this time.3 In addition, the FCC has determined that the CPUC may only require wireline carriers to contribute to a number pool those blocks of 1,000 numbers that are 10% or less contaminated,4 meaning those blocks in which only 100 or fewer numbers are unavailable. However, wireline carriers may also keep a portion of the 10% or less contaminated blocks if those are needed for use within six months. Thus, 1.2 million numbers out of the 6.0 million unused numbers held by companies in the 858 area code are available only to the companies holding those numbers because they are held by wireless carriers, are in blocks that are more than 10% contaminated, or are in blocks 10% or less contaminated but kept for six-month inventory. The study further finds that of the 6.0 million numbers not in use, a maximum of 5.3 million could be made available to companies through pooling if a) the companies donated blocks with higher contamination levels to the future pool, and b) wireless carriers were required to participate in the future 858 number pool. The first table below illustrates the current distribution of numbers assuming that pooling  is in effect in the 858 area code. The second table shows the distribution that would occur if all the recommendations in this report were implemented.
is in effect in the 858 area code. The second table shows the distribution that would occur if all the recommendations in this report were implemented.
Finally, the study notes that companies identify 1.7 million numbers as unavailable. TD staff recommends specific measures the CPUC can employ to ensure that companies use those "unavailable" numbers more efficiently. Given the near doubling of the number of area codes in California, from 1996 to 1999, this vital public resource should be used as efficiently and effectively as possible. The CPUC and the telecommunications industry should strive to minimize the quantity of numbers left "stranded" in company inventories. The 858 Area Code Report recommendations are summarized in Appendix I.
CHAPTER ONE: OVERVIEW OF NUMBERING
A. INEFFICIENT USE AND INCREASING DEMAND FOR NEW NUMBERS IN CALIFORNIA IS CAUSING AREA CODE PROLIFERATION
California is currently experiencing an explosive demand for telephone numbers and area codes. The increased demand for numbers is due to many factors, including competition for local phone service, as well as the popularity of faxes, pagers, cell phones, internet services, etc. California's robust economy and the growth in the state's population also contribute to the increased demand for telephone numbers. This increase in demand is complicated by a number allocation system dating from the 1940s that is inefficient in today's competitive marketplace.
Prior to 1997, one phone company5 provided local telephone service to all customers in a particular area, and new area codes were opened as the population grew. The number of California area codes rose steadily from 3 in 1947 to 13 in 1992, and stayed at that level until January 1997. During the next three years, however, the number of area codes in California nearly doubled. By the end of 1999, California had 25 area codes. The Telecommunications Act of 1996 sought to open competition for the local telephone service market and competitive local phone companies6 began to enter the marketplace, each requiring its own stock of numbers. The traditional system of number allocation was not designed to provide telephone numbers to more than one company.
In the past, when telecommunication companies needed telephone numbers to serve their customers, they received blocks of 10,000 numbers, i.e. prefixes. Because companies were assigned blocks of 10,000 numbers, they may have been assigned more numbers than they needed. For example, under this system, a company with only 500 customers would have received a 10,000 number block, the same quantity of numbers a company with 9,500 customers would receive. Thus, numbers are taken in these large blocks, creating an artificial demand for more numbers, which in turn fuels the need to open more area codes. The need to assign 10,000 numbers is a practice from the past when one telephone company provided service to all customers in its territory. Today, with over 200 telecommunications companies in the state needing numbers to serve customers, and with the limited quantity of numbers available in each area code, this process is no longer an efficient way to allocate numbers.
The rise in demand for numbers combined with the inefficient allocation system for numbers has forced the rapid opening of new area codes throughout the state. Since 1997, the number of area codes in California has nearly doubled to 25. Without the implementation of major number conservation measures, the telecommunications industry had plans underway to add 22 more area codes in California by 2003. With more and more companies needing numbers of their own, new area codes are not necessarily the best solution.
B. 858 HISTORY AND CPUC DECISIONS
The 858 area code is a classic example of area code proliferation in California. The 858 area code was created in 1999 when it was split from the 619 area code. The 619 area code was implemented in 1982 when it was geographically split from the 714 area code. The 714 area code was originally part of the 213 area code, one of the first three area codes in California when the North American Numbering Plan was implemented in 1947. The 213 area code originally covered all of southern California. The 213 area code was reduced in size by the creation of area code 714 in 1951, 805 in 1957, 818 in 1984, 310 in 1992, 858 in 1997, and 562 in 1998. The 858 area code includes the northern part of the San Diego area including the cities of DelMar, La Jolla, Poway, Rancho Bernardo, Rancho Santa Fe, Linda Vista, and Mira Mesa. The 858 area code is contained within the San Diego Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA).
The 619 area code was created in 1982. After sixteen years, the North American Numbering Plan Administrator (NANPA) determined in 1998 that the 619 area code was running short of numbers. Therefore, the NANPA submitted for CPUC consideration an exhaust relief plan containing two alternatives for introducing a new area code into the 619 area, to provide additional numbers for phone company use. The alternatives submitted included two three-way geographic splits. To create a new area code, the options are either splits or overlays. In an overlay, a new area code is created covering the same geographical area as the existing area code. Under CPUC and Federal Communications Commission (FCC) rules, all customers with numbers in either the new or the old area code are required to dial 1 plus the area code plus the seven digit number (known as 1 + 10 digit dialing) to reach any other number in either of the two area codes. The 858 area code was the first phase of the three way geographic split of the 619 area code. The CPUC has deferred implementation of the second phase of the three-way split.
When the first overlay and 1 + 10 digit dialing were implemented in the 310 area code (located in the Los Angeles area) in April of 1999, customers expressed strong objections to the overlay and to the requisite 1 + 10 digit dialing. The CPUC halted the 310 overlay and ten digit dialing in September. In December of 1999, by Decision
99-12-051, the CPUC suspended all overlays previously approved. In that same decision, the CPUC required its Telecommunications Division (TD) staff to study number use to determine the quantity of available, unused numbers in the 858 area code. This report fulfills that requirement.7
1. Code Administration Allocates Prefixes
For those area codes nearing number exhaust, the CPUC has instituted a lottery process to fairly allocate the remaining prefixes among phone companies when demand exceeds supply. There is no 858 lottery. Therefore, companies receive numbers from Code Administration8. For initial prefixes9, there is no restrictions as long as the company is authorized to provide telecommunications services in California. For growth prefixes, companies must meet a 75% fill rate, six-months to exhaust10, and make regular reporting to the FCC. Companies requested and received 112 prefixes in the 858 area code between January 1, 2000 and December 31, 2000. With the CPUC working with companies to reclaim excess prefixes held by companies, companies returned ten unneeded prefixes to the NANPA during the same period, for a net distribution of 102 prefixes. During the first nine months of 2001, twenty two prefixes have been requested and granted and 24 prefixes have been returned to the NANPA, for a net distribution of negative two prefixes. As of September 30, 2001, there were 273 prefixes available for assignment in the 858 area code.11
C. CPUC EFFORTS TO RESOLVE AREA CODE PROLIFERATION
Recognizing the substantial social and economic burdens associated with constant area code changes, the CPUC has taken steps to resolve the numbering crisis. Responding to widespread public outcry over the proliferation of new area codes, the CPUC suspended, beginning in December 1999, all plans for new area codes previously approved. In July 2000, the CPUC adopted number conservation measures, including establishing number pools, fill rates, and sequential numbering.
1. Number Pooling
The CPUC, with FCC approval, has begun number pools in ten area codes, in order to boost the efficiency of phone number allocation. In addition, the CPUC has ordered number pools for an additional four other area codes during 2001.
Number pooling allows telephone companies to receive numbers in smaller blocks than the traditional 10,000 numbers, enabling multiple providers to share a prefix, thereby utilizing this limited resource much more efficiently. The technology that enables the network to support the assignment of smaller blocks is referred to as Local Number Portability or LNP.12 LNP was originally mandated by the FCC as a means to enable customers to retain their telephone numbers when they switch telephone service to another local provider. This same platform is utilized for number pooling. The FCC had required all wireline carriers to become LNP-capable by the end of 1998 in the largest 100 Metropolitan Statistical Areas (MSAs) in the country. Thirteen of the top 100 MSAs are located in California; the 858 area code is located in one of them.13
Though LNP technology has existed for several years, the FCC later granted cellular and PCS companies an extension of time until November 2002 to become LNP-capable. The FCC gave paging companies a permanent exemption from the LNP requirement.14 Thus, at this time only wireline carriers15 can participate in number pooling. In the area codes with number pooling, wireline carriers participate in pooling and wireless carriers participate in the lottery or receive prefixes from Code Administration (if no lottery). In the remaining area codes with rationing in effect, all phone companies participate in the lottery.16
The CPUC has been aggressively setting up number pools. In November 2000, by an Assigned Commissioner's Ruling, the CPUC established a schedule for ten number pools for 2001. The CPUC also issued a more detailed schedule in February 2001 identifying the start dates for the nine number pools scheduled to begin in 2001. A pooling schedule has not yet been set for the 858 area code. Once pooling is implemented in the 858 area code, all wireline companies with numbers in rate centers located in top 100 MSAs in 858 will be required to donate 1,000-number blocks to the pooling administrator. While FCC rules only require companies to donate numbers to a number pool in rate centers located in top 100 MSAs, many companies have implemented LNP capability throughout their service territories. These companies could also donate or receive thousand-blocks in all rate centers in an area code's number pool, rather than just in the rate centers located within top 100 MSAs. Under the number pooling program, all LNP-capable carriers will receive numbers in blocks of 1,000 on an as-needed basis. There is no rationing process in the pool and the blocks received can be put into service almost immediately upon receipt. All wireless carriers, as well as wireline carriers who decline to take part in pooling in the rate centers not located in a top 100 MSA, will continue to receive numbers in blocks of 10,000 through the monthly lottery allocation process or from Code Administration in area codes without a lottery process.
2. Improved Number Inventory Management
While number pools have improved the efficiency of the distribution of numbers to companies, companies have not had strong incentives to efficiently manage the numbers already allocated to them. Thus the CPUC ordered companies to improve number inventory management with measures including rules on fill rates and sequential numbering.
In July 2000, the CPUC issued Decision 00-07-052, which extended number conservation measures adopted in the 310 area code to other area codes within California. These number conservation measures include the following:
· Companies are required to return to the NANPA any prefix held for more than six months without being used.
· "Imminent exhaust criteria" are established in all area codes with lotteries or number pools. In each rate center in which companies request additional numbers, they must provide to the NANPA a form demonstrating they will be out of numbers within six months.17
· Companies must satisfy a minimum 75% fill rate requirement before being eligible to request a growth prefix in any area code in rationing and before being eligible to receive a thousand-block through a number pool. Companies must assign numbers in thousand-block sequence, assigning numbers in the next block only once a 75% fill rate has been attained in the prior block.
TD anticipates these policies will potentially free more numbers for use in number pooling, to be allocated through the lottery or from Code Administration, or to be otherwise used by companies. Indeed, these measures together with the effects of number pooling have already achieved some positive effects. For example, since the CPUC extended the 75% fill rate and imminent exhaust rules to all area codes, request for prefixes by companies have dramatically declined. Another positive outcome is the recent increase in the number of prefixes in the 858 area code being returned to NANPA by companies as mentioned in Section B.1 above.
3. CPUC Efforts at Federal Level
The FCC has exclusive jurisdiction over numbering in the United States. Therefore, the CPUC's number conservation policies (pooling, fill rates, and sequential numbering) are governed by the FCC's delegation of authority to the states. In recognition of the severity of the numbering crisis in California, the CPUC has aggressively petitioned the FCC for additional authority. As a result, the FCC has delegated authority to plan and implement area code changes, as well as authority to implement number conservation measures.
a. Authority Regarding Pooling
On April 26, 1999, the CPUC filed a petition with the FCC requesting authority to institute number pools and other number conservation measures within the state to better manage this public resource. On September 15, 1999, the FCC granted that petition, allowing the CPUC to institute mandatory number pooling on a trial basis, deploying it sequentially in one MSA at a time. When the FCC granted the CPUC the authority to deploy various numbering resource optimization strategies, including the authority to institute thousand-block numbering pooling trials, it also clarified that California's authority will be superseded by future national measures adopted by the FCC.
On March 31, 2000, the FCC released the Numbering Resource Optimization Report and Order and Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (first NRO Order).18 The first NRO Order sets forth rules for defining numbers, forecasting, tracking and auditing companies' use of numbers, and for conservation measures associated with number usage, including but not limited to number pooling. The definitions of numbers and timelines for aging and reserved numbers that were adopted in that order have been incorporated into the utilization data cited herein.
With the release of the first NRO Order, the FCC adopted a number of administrative and technical measures that will allow it to monitor more closely the way numbering resources are used and to promote more efficient use of numbering resources. In particular, the FCC adopted a nationwide system for allocating numbers in blocks of one thousand, rather than ten thousand, wherever possible, and announced its intention to establish a plan for national rollout of thousand-block number pooling.
Because the FCC recognized that state thousand-block number pools underway might not conform to the national standards set forth in the first NRO Order, the FCC gave state commissions until September 1, 2000 to conform their thousand-block number pools to the national framework. One requirement imposed in California which differs from the national standards is the requirement that companies meet a 75% fill rate in each block before they may receive an additional block from the pooling administrator. The CPUC recognized the 75% fill rate as a critical factor in the success of the 310 pooling trial and petitioned for a waiver of compliance with the national rules. On August 31, 2000, the FCC issued an order granting the CPUC authority to continue to use its pooling rules until the FCC decides on the merits of the petition, or until December 31, 2000, whichever occurs sooner. This allowed California to continue applying the 75% utilization rate in its number pooling efforts.
On December 29, 2000, the FCC issued its Second Report and Order on Number Resource Optimization. In the second NRO Order, the FCC ruled on California's Petition for Waiver, concluding that the CPUC may continue to use its utilization thresholds subject to parameters set in this order (when FCC thresholds exceed California's, California must migrate to the more stringent utilization thresholds). The FCC also declined to adopt a transition period between the time that cellular carriers must implement LNP and the time they must participate in any mandatory number pooling.
The first NRO Order further constrains the CPUC by concluding that the rollout of thousand-block number pooling should first occur in area codes that are located in the largest 100 MSAs. In its comments prior to the release of the first NRO Order, the CPUC had argued that California would be precluded from exploring whether number pooling could alleviate the crises for number resources in many parts of the state that are located outside the top 100 MSAs. The CPUC believes the FCC should delegate authority to the states to order deployment of LNP. This grant of authority to California would make pooling possible throughout the state.
b. Authority Regarding Technology-Specific Area Codes
Currently, state commissions are constrained by the FCC from establishing an area code specifically for wireless telecommunications services. On April 26, 1999, the CPUC filed another petition with the FCC requesting authority to create service-specific or technology-specific area codes. In the 858 area code, there are fifteen wireless carriers holding 60 prefixes. If the CPUC were allowed to create a separate area code for those companies, these 60 prefixes in the 858 area code could be reassigned to other phone uses, thus prolonging the life of the existing area code. To date, the FCC has not acted on the CPUC's petition. In the Second Report and Order, the FCC asks for further comments on technology-specific or non-geographic area codes.
On September 28, 2000, Governor Davis signed into law Senate Bill (SB) 1741, authored by Senator Bowen. SB 1741 requires the CPUC to request authority from the FCC to require telephone corporations to establish technology-specific area codes based on wireless and data communications, and to permit 7-digit dialing within both that technology-specific area code and the underlying pre-existing area code or codes. The bill requires the CPUC to use any authority so granted unless it makes a specified finding that there is reason not to do so. The legislation also prohibits the CPUC from implementing any authority granted by the FCC in a manner that impairs number portability. The petition that the CPUC filed with the FCC in April 1999 fulfills the technology-specific area code requirement set forth in the bill. The bill also prohibits the CPUC from approving new area codes unless a telephone utilization study has been performed and all reasonable telephone number conservation measures have been implemented.
4. Utilization Studies
Before requiring the residents and businesses of the 858 area code to undergo another area code change, the CPUC recognized the necessity of determining the number of telephone numbers that are in use and the number yet to be used. To that end, the CPUC required companies to provide usage data to the CPUC as of December 31, 2000. The TD contracted with NeuStar to collect the data; NeuStar submitted the aggregated data in its entirety to TD in April 2001. The definitions used in the utilization study and a list of companies holding prefixes in the 858 area code are in Appendix A.
CHAPTER TWO: 6.0 MILLION UNUSED NUMBERS IN THE 858 AREA CODE
Of the 7.7 million numbers in the 858 area code, companies hold 3.7 million. The other 4.0 million numbers have yet to be assigned to companies. The CPUC's utilization study found that, of the 3.7 million numbers held by companies, 2.0 million remain unused in their inventories. Therefore, 6.0 million numbers in the 858 area code remain unused. A portion of these unused numbers can be made available for use by all companies, either through pooling in the future or through allocation from Code Administration. In addition, companies have reported 1.7 million numbers as unavailable. A portion of these unavailable numbers can be used more efficiently if the recommendations contained in this report are implemented.
A. THE SCOPE OF THE UTILIZATION STUDY
5. Distribution Statistics of Prefixes
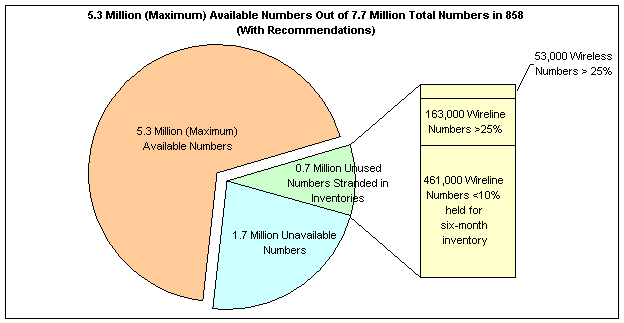
The CPUC asked 40 companies, holding 370 prefixes (3.7 million numbers) in the 858 area code, to report their utilization data, with a reporting cutoff date of December 31, 2000. Table 2-1 shows the distribution of these prefixes by type of carrier: incumbent local exchange carrier (ILEC), competitive local exchange carrier (CLEC),19 paging carrier, and cellular/PCS carrier.
6. Companies Reporting
Of the 40 companies in the 858 area code, 37 submitted utilization data. A list of the companies that have been allocated numbers in the 858 area code appears in Appendix A-2.
7. Non-Reporting Companies
The remaining three companies hold nine prefixes in the 858 area code. TSR Wireless, Net-Tel Corp.-CA, and Prism California Operations informed NeuStar that they were out of business in California.
D. 6.0 MILLION NUMBERS AVAILABLE IN THE 858 AREA CODE
The 858 area code has 6.0 million unused numbers. Of these unused numbers, TD found that companies held 2.0 million numbers in their inventories.20 These numbers held in inventory are currently not used for any purpose but held in anticipation of future need. The remaining 4.0 million unused numbers are not yet assigned to companies; 2.7 million numbers are available for allocation from Code Administration in the 858 area code and 1.3 million numbers have been set aside for number pooling. The summary of available numbers is shown in the table below.
Table 2-2
Summary of Available Numbers
Wireline Carriers 1,594,659
Wireless Carriers 372,881
Type 1 Carriers21 26,532
Total Available/Unused Numbers Held by Companies 1,994,072
Numbers Available for Allocation from Code Administration 2,680,000
Numbers Set Aside for the 858 Number Pool 1,340,000
Total Available Numbers in the 858 Area Code 6,014,072
Not all of the 6.0 million unused numbers are immediately available to every company that wants numbers. Of the 6.0 million, a maximum of 4.8 million numbers22 are estimated to be available to all companies via a future number pool or from Code Administration. The remaining 1.2 million numbers are only available to the companies that hold them. As shown in the table below, the CPUC could shift the availability of numbers from one category to the other by adopting the recommendations23 in this report. Of the 6.0 million unused numbers, those actions could result in making a maximum of 5.3 million numbers24 available to all companies, with the remaining 0.7 million numbers available to the companies that hold them.

Current technology requires a company to be LNP capable in order to donate numbers for another company to use. All wireline carriers in the 858 area code are required to be LNP capable.25 Wireline carriers hold 1.6 million unused numbers in the 858 area code. In order for the unused numbers to be retrieved from company inventories, the FCC requires these unused numbers to be retrieved from blocks which are 10% or less contaminated.26 Of wireline companies' 1.6 million unused numbers, 1.3 million are contained in 1,275 thousand-blocks that are 10% or less contaminated. However, not all of these 1.3 million numbers can be retrieved from companies' inventories because companies need to have enough numbers to meet anticipated future need.27 Both the CPUC and the FCC have determined that six months of inventory is a reasonable quantity to hold for future use. TD will not know how many of these 1.3 million numbers will be available for pooling until companies submit their pooling block donations to the pooling administrator in November of 2001 (although the exact milestone dates for the 858 pool have not yet been established).28 In the meantime, a reasonable estimate of numbers likely to be donated to the 858 pool, based on the experience of the 310 pool, is 789,00029. The difference between the potential maximum 1.3 million currently pool-able numbers that wireline carriers hold and the 789,000 numbers estimated as likely to be donated to the pool consists of an estimated 461,000 numbers that companies will need for their six-month inventories.
The remaining 345,000 of the 1.6 million unused numbers cannot be retrieved, either because the numbers are in blocks more than 10% contaminated or because they are in non-LNP-capable blocks. However, companies can immediately use these numbers to provide service to their customers or meet other needs. Wireline carriers hold 252,000 numbers in blocks that are more than 10% contaminated.30 Wireline carriers hold another 93,000 unused numbers in blocks that are non LNP-capable.
Wireless carriers hold 373,000 unused numbers in the 858 area code. Of these unused numbers, 310,000 are in blocks that are 10% or less contaminated and 63,000 numbers are in blocks more than 10% contaminated. Until wireless carriers become LNP capable in November 2002, none of these numbers may be reallocated to other companies. In the interim, wireless carriers may assign these numbers to their own customers.
E. ANALYSIS OF AVAILABLE NUMBERS
1. Analysis of Wireline Carriers' Contamination Rates
The CPUC requires each company participating in number pools to donate blocks that are 10% or less contaminated, excluding those retained for the company's six-month inventory.31
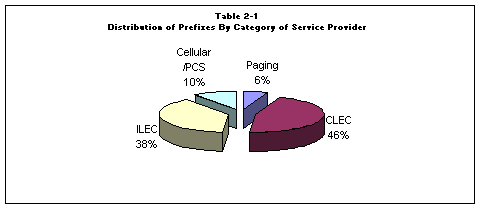
TD analyzed the 858 utilization data to determine the availability of numbers within blocks of different contamination rates in order to assess different contamination thresholds that the CPUC could apply to number pools. The following table summarizes available numbers by contamination level, by rate center, for wireline carriers.
________________________________________________________________________
Table 2-4
Available Numbers by Percentage Contamination for LNP Capable Wireline Carriers
Rate Center |
0% |
>0% to 10% |
>10% to 15% |
>15% to 20% |
>20% to 25% |
DELMAR |
107,000 |
64,589 |
7,068 |
800 |
1,595 |
LA JOLLA |
134,000 |
75,116 |
7,861 |
4,863 |
6,243 |
POWAY |
89,000 |
39,019 |
4,399 |
2,400 |
798 |
RANCHO BERNARDO |
115,000 |
56,504 |
3,515 |
4,038 |
3,919 |
RANCHO PENASQUITOS |
80,000 |
25,263 |
0 |
3,206 |
774 |
RANCHO SANTA FE |
63,000 |
17,455 |
0 |
1,600 |
0 |
SAN DIEGO: LINDA VISTA DA |
116,000 |
70,623 |
7,935 |
6,575 |
3,925 |
SAN DIEGO: MIRA MESA DA |
144,000 |
63,220 |
5,315 |
4,901 |
788 |
GRAND TOTALS |
848,000 |
411,789 |
36,093 |
28,383 |
18,042 |
The first two numeric columns of Table 2-4 show the potential numbers available to a future number pool, except for those numbers kept for companies' six-month inventory, under current rules. Available numbers in one rate center cannot be used in another rate center. Table 2-4 shows that all rate centers have available numbers that companies could donate to the pool.
The last three columns of Table 2-4 capture available numbers in blocks that are more than 10% contaminated but no more than 25% contaminated. Under the current number pool rules, companies retain thousand-number blocks that are more than 10% contaminated. Increasing the contamination rate threshold for donations from 10% to 25% would potentially free up an additional 83,00032 numbers for use in a number pool. TD cautions that, although Table 2-4 shows potential results from increasing allowable contamination levels, further analysis and input from the industry would be necessary to determine accurately the quantity of additional blocks that could be added to the pool while still leaving companies with a six-month inventory.
As shown by Table 2-4, and also shown graphically in Table B-3 of Appendix B, all rate centers have available numbers from blocks of differing contamination levels up to 25%. The tables show that if the contamination ceiling for pooling were increased from 10% to 25%, more unused numbers exist in all rate centers that potentially could be donated to the pool.
Recommendation from Block Contamination Analysis of Wireline Carriers
· The CPUC should petition the FCC to increase the contamination level for pooling to 25%. If the FCC grants the petition, the CPUC should increase the maximum contamination level of donated blocks from 10% to 25% for all LNP-capable carriers.
2. Analysis of Wireless Carriers' Contamination Rates
Under current FCC rules, cellular and PCS companies are exempt from number pooling until November 2002 when they must become LNP capable. The FCC has indefinitely exempted paging companies from the LNP requirement. Table 2-5 shows available numbers in blocks of differing contamination levels held by wireless carriers. Wireless carriers hold 310,000 available numbers in blocks that are 10% or less contaminated, as shown in the first two numeric columns of Table 2-6. Wireless carriers also have 10,000 available numbers in blocks with contamination levels greater than 10% but less than or equal to 25%, as indicated by the last three columns of Table 2-5. Of these 320,000 unused numbers held by wireless carriers, TD estimates that 162,000 (50.66%) are held by paging companies33. TD staff is investigating whether there are methods to make some of these 162,000 unused numbers available to other carriers despite the FCC's exemption of paging companies from the LNP requirement.
Table 2-5
Available Numbers by Percentage Contamination for Wireless Carriers
Rate Center |
0% |
>0% to 10% |
>10% to 15% |
>15% to 20% |
>20% to 25% |
DELMAR |
33,000 |
16,673 |
0 |
0 |
799 |
LA JOLLA |
49,000 |
27,223 |
2,653 |
1,620 |
0 |
POWAY |
41,000 |
20,635 |
1,719 |
0 |
1,532 |
RANCHO BERNARDO |
23,000 |
2,891 |
888 |
846 |
0 |
RANCHO PENASQUITOS |
19,000 |
902 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
RANCHO SANTA FE |
19,000 |
900 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
SAN DIEGO: LINDA VISTA DA |
36,000 |
1,901 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
SAN DIEGO: MIRA MESA DA |
19,000 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
GRAND TOTALS |
239,000 |
71,125 |
5,260 |
2,466 |
2,331 |
_______________________________________________________________________
Because the FCC has granted wireless carriers an extension of time to implement LNP, no wireless carriers serving the 858 area code have implemented LNP. Thus, wireless carriers cannot participate in number pooling at this time, resulting in 320,000 unused numbers in blocks between 0% and 25% contamination in the 858 area code.
Further analysis of the utilization data submitted by wireless carriers reveals sharply different utilization rates of paging carriers and cellular/PCS companies. While cellular/PCS companies in the 858 area code are using 42% of their numbers (counting assigned numbers only), paging carriers' data shows a utilization rate of only 9%. Paging carriers reported an additional 5% of their numbers used for administrative, intermediate, reserved and aging purposes, yielding a total percentage of unavailable numbers of 14%. Cellular/PCS companies reported 10% of their numbers used for these miscellaneous purposes, bringing their total percentage of unavailable number to 52%. Thus, 86% of the numbers held by paging companies are unused, while 48% of the numbers held by cellular/PCS companies are unused.
Recommendations from Block Contamination Analysis of Wireless Carriers
· When cellular and PCS companies become LNP capable in November 2002, the CPUC should direct those wireless carriers to donate to and participate in all number pools in California, using the same contamination threshold for donated blocks in effect for all LNP-capable companies.
· The CPUC staff should meet with paging companies to explore options for consolidating numbering resources in fewer rate centers, as well as other methods of reducing the number of stranded numbers held by paging companies.
3. Potential Block Contamination Abuses
When blocks are slightly more than 10% contaminated, those blocks cannot be donated to a pool under current pooling rules. Viewing the utilization data suggests, that companies have not generally followed practices of sequential numbering and filling blocks substantially before using new blocks. The CPUC's rules on sequential numbering and fill rate practices promulgated in Decision 00-07-052 are designed to ensure that companies efficiently use their numbers in the future. Fill rates mitigate contamination by requiring companies to use contaminated blocks up to 75% before they can receive additional blocks or prefixes. Sequential numbering minimizes contamination by requiring companies to begin assignment in the next thousand-block only after a 75% fill rate has been attained in the prior block. Where companies possess significant available numbers in a given rate center, these two efficiency measures could prevent the opening of new blocks or prefixes.
Companies reported utilization data as of December 31, 2000. The sequential numbering and fill rate decision was issued in July 2000. Some of these practices of non-sequential numbering and not filling blocks substantially before using new blocks may have happened before the July 2000 decision. TD does not expect companies to continue contaminating blocks unnecessarily.
Recommendations for Block Contamination Issues Affecting All Carriers
· The CPUC should monitor compliance with its fill rate and sequential numbering policies through future number utilization filings and audits.
*0 The CPUC should establish penalties for non-compliance with fill rate and sequential numbering policies adopted in Decision 00-07-052.34
4. Reclamation of Prefixes
Decision 00-07-052 directed companies to return prefixes that are held unused for more than six months. As shown in Appendix B-1, wireline carriers and wireless carriers hold 922,000 unused numbers and 239,000 unused numbers, respectively, in 0% contaminated blocks. Of these unused numbers, 240,000 are in 24 whole prefixes35 that are completely uncontaminated, i.e., spare prefixes, while 921,000 numbers are in uncontaminated blocks that are scattered throughout many different prefixes. The following table shows the breakdown between wireless and wireline carriers.
Table 2-7
Breakdown of Numbers in 0% Contaminated Blocks
Avail. Nos. in Avail. Nos. in Avail. Nos. in
0% Contam. Blocks Spare Prefixes Differing Prefixes
Wireline Carriers 922,000 140,000 782,000
Wireless Carriers 239,000 100,000 139,000
Total 1,161,000 240,000 921,000
The 240,000 numbers in 24 spare prefixes can possibly be reclaimed if not used within six months. However, as a result of the FCC's March 31, 2000 (first) NRO Order, the NANPA no longer has sole authority to reclaim unused prefixes. The FCC granted authority to state regulatory commissions to investigate and determine whether prefix holders have activated prefixes within the allowed time frames, and directed the NANPA to abide by the state commission's determination to reclaim a prefix if the state commission is satisfied that the prefix holder has not activated the prefix within the time specified in the first NRO Order.36 Substantial cooperation between the CPUC and the NANPA will be required in order for the CPUC to exercise this new authority and determine whether a prefix should be reclaimed. Furthermore, the NANPA must still perform the mechanical steps to reclaim prefixes once the CPUC directs the NANPA to reclaim a prefix.
The NANPA has provided to the CPUC a list of companies that have failed to report whether their assigned prefix(es) have been placed in service. The CPUC issued Assigned Commissioner's Ruling Requiring Carriers to Comply With NXX Code Reclamation Rules, dated December 21, 2000. In this ruling, the CPUC instructed the delinquent companies to comply immediately. Companies are to inform the CPUC either that the prefix(es) have been placed in service or returned, that the company was incorrectly included in the NANPA's delinquent list, or the reasons the prefix(es) have not been placed in service. The CPUC will review the reasons and make a determination as to whether the prefix(es) must be returned or reclaimed by the NANPA, or whether to grant an extension of time to the company to place the prefix(es) in service. Any delinquent company that fails to comply will be subject to penalties and sanctions.
F. ANALYSIS OF 1.7 MILLION UNAVAILABLE NUMBERS
In the following sections, TD recommends a series of policies designed to require companies to use unavailable numbers more efficiently. These policies would potentially free more numbers for use in the future 858 number pool, to be allocated from Code Administration, or to be used otherwise by companies.
Companies report that 1.7 million numbers in the 858 area code are either assigned to customers or are used by companies for reserved, administrative, intermediate and aging purposes. Companies commonly refer to these numbers as "unavailable". Unavailable numbers include not only those actually in use by customers, but also the following categories:
· Reserved numbers - Numbers that are reserved in blocks for future use by specific customers;
· Administrative numbers - Numbers that companies use for their own internal purposes;
· Intermediate numbers - Numbers that are made available for use by another telecommunications carrier or non-carrier entity for the purpose of providing telecommunications service to an end user or customer; and
· Aging - Numbers from recently disconnected service, which are not reassigned during a fixed interval.
In its first NRO Order, the FCC ruled that companies must show that they have used a certain percentage of their existing inventory of numbers before they may obtain additional numbers in a given rate center. This order specified that companies' utilization rates will be calculated using only assigned numbers in the numerator. This method greatly increases companies' incentive to use number sparingly for purposes of reserved, administrative, intermediate, or aging numbers; none of those uses will raise a company's utilization rate and enable it to obtain additional numbers.
1. 1.4 Million Assigned Numbers
In the 858 area code, there are 1.4 million assigned numbers, with 1.2 million assigned to customers by wireline carriers and 0.2 million assigned to customers by wireless carriers. The percentages of assigned numbers to total numbers held by companies are shown in the table below.
Table 2-8
Assigned Numbers to Numbers Held by Companies (in millions)
________________________________________________________________________
Numbers Percentage
Assigned Numbers Held by Companies Assigned
Wireline Carriers 1.2 3.1 39.96%
Wireless Carriers 0.2 0.6 29.82%
a. Non-Working Wireless
Non-Working wireless describes numbers assigned to wireless customer equipment, but which are not yet working. These numbers are considered a sub-category of assigned numbers. For example, wireless carriers sometimes pre-package a cellular telephone with an assigned telephone number for sale to customers. Although the number is assigned, it will remain inactive until a customer purchases the telephone. There are no non-working wireless numbers reported for this area code. While the quantity of non-working wireless numbers reported generally is low, this sub-category of assigned numbers could increase because there are no restrictions on the number of days that a wireless company can hold these numbers, causing numbers to remain idle for an unspecified period.
The CPUC should consider several options to improve inventory management of non-working wireless numbers. One option is for the CPUC to require companies to return these numbers to the available category after 180 days (similar to the requirement the FCC has established for reserved numbers). Since pre-packaged equipment with non-working assigned numbers is often located in various retail outlets, another option is for the CPUC to require companies to maintain inventory records of all such retail/wholesale equipment with the associated numbers assigned and to require regular (weekly/monthly) updating of these inventory records.
Recommendations for Treatment of Non-Working Wireless
· Non-working wireless numbers should be treated as reserved numbers and limited to 180 days, after which they should be classified as available for assignment to customers.
· The CPUC should continue to monitor non-working wireless numbers in the near term by reviewing future utilization filings, and should include this category of numbers in any audits conducted of wireless carrier number use.
b. Eliminating Interim Number Portability Releases Numbers for Reallocation
Interim Number Portability (INP) is the ability to move telephone service from one service provider to another using Remote Call Forwarding (RCF), Direct Inward Dialing (DID), or equivalent means. 37 Prior to the implementation of permanent LNP, companies entered into INP arrangements to enable the transfer of customers from one company to another. Under these INP arrangements, two telephone numbers are associated with each customer. LNP eliminates the need for two telephone numbers for each customer when the customers change companies because customers can take their numbers with them.
Since the 858 area code is included in one of the top 100 MSAs in the nation, all wireline carriers should be LNP-capable. The only companies that reported INP numbers were ILECs. They reported a total of 275 numbers in the 858 area code. Since all the reported INP numbers were from ILECs and none were from their competitors, it does not appear that INP exists in the 858 area code to facilitate competition for customers. Thus, TD questions why any INP numbers exist in this area code. Switching to LNP technology and eliminating INP will free up half of the 275 numbers that are currently dedicated to INP.
Recommendations for INP-Related Conservation Measures
· The CPUC should require companies to transition from INP to LNP in the 858 area code and implement a monitoring mechanism to ensure compliance.
· The CPUC should adopt a schedule for transitioning INP arrangements to LNP in all other California area codes.
c. Expanded Use of the 555 Prefix Could Release Other Prefixes Dedicated to Special Uses
Historically, the telecommunications industry has designated certain prefixes for special uses, usually to an ILEC. These include numbers for recorded public information announcements such as time-of-day, weather forecasts, high-volume call-in numbers, and emergency preparedness38 numbers. These prefixes are not made available for general commercial use, and thus numbers within these prefixes that are not in actual use lie vacant. In 1999, companies decided not to duplicate the special use prefixes in each area code. Concerned that this process could adversely affect the public, the CPUC directed that these prefixes should be duplicated in each new area code.
The utilization study shows that 4 prefixes are dedicated for special uses: one each for directory assistance, high volume calling, time, and weather service. TD questions the necessity of assigning an entire prefix for each of the purposes listed above.
Furthermore, having multiple special use prefixes is an inefficient use of numbers in the 858 area code as well as in other area codes in California. For example, if the 555 prefix39 currently reserved only for directory assistance could be used to provide time and emergency preparedness then two more prefixes could be returned for reallocation in the 858 area code.
Similarly, expanded use of the 555 prefix throughout the state could result in more returned prefixes in other area codes. TD recommends that the CPUC initiate an investigation into broader use of the 555 prefix in California. The CPUC should further analyze the option of obtaining standard 555 numbers in every California area code to provide time, emergency preparedness, and weather information at no additional cost to customers.
Recommendations for Special-Use Prefixes
· TD recommends that the CPUC initiate an investigation into the possibility of moving the numbers for time and emergency preparedness into the 555 prefix.
· TD recommends that the CPUC include in its investigation the broader use of the 555 prefix in California's area codes by providing standard 555 numbers in every California area code to provide time, emergency preparedness, and weather information.
2. Reserved Numbers Are a Potential Source of Additional Numbers
Carriers "set aside" numbers for future use by customers.40 Previously, industry number assignment guidelines allowed companies to reserve a prefix for up to 18 months for customers' future use.41 The FCC's first NRO Order modified the number reservation period to 45 days. This 858 utilization study incorporated the FCC's 45-day requirement. The FCC later issued an extension until December 1, 2000 for companies to comply with the 45-day rule. 42 The extension allows companies time to upgrade their number tracking mechanisms, which tally the quantities of reserved numbers they hold. The FCC's second NRO Order on Reconsideration changed the number reservation period to 180 days. This took effect on December 29, 2000.43 Companies reported a total of 92,400 reserved numbers in the 858 utilization study. 44
Wireline carriers reported a total of 80,255 reserved numbers in the 858 area code. If the quantity of reserved numbers held by wireline carriers can be minimized, additional numbers could be available for immediate use by the companies from within their own number inventories thus slowing the rate at which new prefixes are allocated to these companies. Numbers could also be freed up for reallocation in the 858 number pool. Currently there are no imitations on the quantity or percentage of numbers a company can classify as reserved before requesting new numbers. Similarly, companies are not required to use their reserved numbers stock before they can request that new numbers be allocated to them. Comparing the data on Rancho Penasquitos rate center and the Poway rate center illustrates wide discrepancies between the quantity of reserved numbers companies hold. The Poway rate center has 21 prefixes and 5,690 reserved numbers while the Rancho Penasquitos rate center has 17 prefixes and only 638 reserved numbers. If the CPUC orders efficient use practices specific to reserved numbers, more numbers could be made available for customer use.
Wireless carriers reported 12,189 reserved numbers in the 858 area code. Wireless carriers also reported wide variances in reserved numbers. Comparing the data on the Poway rate center and the La Jolla rate center illustrates wide discrepancies between the quantity of reserved numbers companies hold. The La Jolla rate center has 18 prefixes and 6,022 reserved numbers while the Poway rate center has 17 prefixes and only 153 reserved numbers. As with wireline carriers, efficient number use practices specific to reserved numbers could immediately free up numbers within these companies' inventories for use, and thus, could slow the rate at which new prefixes are allocated to these companies. Once wireless carriers are able to participate in number pooling, these practices could have the same efficiency gains as those for wireline carriers.
Recommendations for Reserved Numbers
· The CPUC should monitor reserved number use for all companies by reviewing future utilization data to ensure companies are complying with the FCC's 180-day requirement.
3. Restrictions on Administrative Numbers Could Yield More Numbers
Administrative numbers are those not assigned to customers and are generally used for a wide range of applications for companies' internal use, including testing, internal business, and other network purposes. Companies reported almost 59,000 administrative numbers in the 858 area code. Wireline carriers hold approximately 51,000 of these numbers and wireless carriers hold approximately 8,000 of them.
The utilization study revealed that there is a potential for companies to over-assign administrative numbers within a particular thousand block, prefix or rate center in the 858 area code. The following example demonstrates the potential for over-assignment. In the San Diego Linda Vista rate center, a company is using 1,482 numbers for administrative purposes in one prefix while the average across all companies is 160. Given the variances in the levels of administrative numbers between companies and rate centers, it is unclear what basis companies use for placing numbers in this category. The CPUC should therefore pursue an investigation in this area.
In addition, some companies randomly assign administrative numbers and are thereby wasting number resources. Companies could conserve numbers by changing the way in which these types of numbers are assigned. Some companies randomly assigned administrative numbers in multiple thousand-blocks within the same prefix when they have available number resources to centralize those assignments within one or a few blocks. This practice means that both wireline and wireless carriers will already have contaminated multiple thousand-blocks and prevents them from donating blocks once they can participate in number pooling, or from other LNP-based conservation measures.
Also, some companies holding multiple prefixes in a given rate center randomly assign administrative numbers throughout different prefixes when they have the available number resources to centralize the assignment of these numbers in one prefix in that rate center. TD questions the need for companies to hold multiple prefixes in a given rate center, when they are using multiple prefixes to serve their internal purposes and not necessarily to serve customer needs.
As stated in section D above, under the utilization rules promulgated in the FCC's First and Second NRO Orders, carriers now have a much stronger incentive to minimize the quantity of numbers they use for administrative purposes, thus freeing more numbers for immediate assignment to customer, or for donation to the number pool.
4. Intermediate Numbers
The "intermediate number" category was only recently introduced by the FCC in its first NRO Order. This category tracks numbers that companies make available for use by another telecommunications carrier or non-carrier entity. Companies reported a total of approximately 85,000 intermediate numbers in the 858 area code. Wireline carriers hold about 70,500 of those numbers and wireless carriers hold around 14,500. The quantity of intermediate numbers varied significantly among rate centers in the 858 area code. 45 Since the intermediate number category is new, the quantity of numbers reported by companies may increase over time as more companies become familiar with this category. TD notes that this number use category has the potential for abuse by companies if they use significant quantities of number resources for intermediate purposes. Therefore, TD recommends the CPUC continue to monitor intermediate number use.
Recommendation for Intermediate Numbers
· The CPUC should monitor intermediate number use for all companies by reviewing future utilization filings to test whether potential abuses in this reporting category occur.
a. Type 1 Numbers
Wireline carriers allocate numbers for use by wireless carriers through Type 1 interconnection agreements.46 Because wireline and wireless carriers share responsibility for Type 1 numbers, both types of companies reported on these numbers. Wireline carriers report Type 1 numbers in the Intermediate category since they provide these numbers to another company. Wireline carriers also list the wireless carriers to whom they distributed ranges of numbers. Wireless carriers report on the numbers they received, placing them in the Assigned, Administrative, Reserved, Intermediate, Aging, or Available categories.
Record keeping of Type 1 numbers is inadequate because, more often than not, wireline carriers' reports disagreed with wireless Type 1 carriers' reports. In the 858 area code, over half of all Type 1 numbers are unaccounted for or mismatched.47 In some cases, wireless Type 1 carriers deny "owning" the numbers that wireline carriers report as distributed. In other cases, wireless Type 1 carriers go out of business and do not return their numbers to the wireline carrier. In either case, numbers are lying dormant, used by neither the wireline or wireless Type 1 carrier.
In today's scarce numbering environment, it is unacceptable to let numbers go unused because of inadequate record keeping. Wireline donor carriers currently do not monitor wireless Type 1 inventories, nor do they proactively reclaim unused Type 1 numbers from wireless carriers. TD recommends that wireline carriers perform a one-time inventory check on Type 1 numbers to confirm that the numbers they have distributed are acknowledged by the recipient wireless Type 1 carrier. If errors are discovered, the wireline carriers should count the numbers as part of their own inventories.
Improved Type 1 number management is particularly crucial because unlike numbers held by most wireless carriers, Type 1 numbers are eligible for number pooling.48 Therefore, once wireline carriers recover unused Type 1 numbers, these numbers could be made available for pooling. The CPUC should recognize Type 1 numbers as a resource for number pooling and take steps to have wireline companies recover unused Type 1 numbers for donation to the number pool.
As described in Chapter 1, state and federal mandates require most companies to demonstrate efficient numbering practices before becoming eligible to obtain more numbers. In contrast, Type 1 wireless carriers have no check on their number use because they draw numbers directly from wireline companies, therefore avoiding the scrutiny of the official number administrator. TD recommends that Type 1 wireless carriers be subject to number conservation measures, and the CPUC should develop a system to ensure compliance.
Recommendations for Type 1 numbers:
· Wireline and wireless carriers should improve Type 1 number inventory management. Wireline carriers should perform a one-time inventory check of wireless Type 1 numbers to verify their records match that of the wireless Type 1 carriers' records. Companies should make inventory data available to the CPUC upon request. Wireline carriers should recover and add to their inventories any Type 1 numbers lying dormant.
· Type 1 carriers should be subject to number conservation techniques such as sequential numbering and fill rates. A system to ensure compliance with Type 1 number conservation measures should be developed.
· The Commission should consider Type 1 numbers as potential donations to the number pool. Excess and unused Type 1 numbers should be returned to the wireline carriers and either used to serve customers or donated to the number pool.
5. Aging Numbers
The FCC's first NRO Order defines aging numbers as disconnected numbers that are not available for assignment to another customer for a specified period of time. Consistent with the Industry Numbering Committee (INC) Guidelines, the CPUC adopted the FCC upper limits for aging numbers as 90 days for residential numbers and 365 days49 for business numbers.
In the 858 area code, there are approximately 78,000 numbers in the aging category, representing 4.48% of the total unavailable numbers.
A higher percentage of aging numbers occurs in the wireless category, as compared to the wireline category. Aging numbers represent 5.67% of the total unavailable wireless numbers, or about 13,000 numbers. Aging numbers represent 4.30% of the total unavailable wireline numbers, or about 65,000 numbers. This is consistent with the higher turnover or "churn" that occurs in the wireless industry. Appendix G shows the breakdown of aging numbers by wireless and wireline categories.
· Although the CPUC has required all companies to differentiate aging numbers between residential and business and track the two categories separately, Pacific Bell has not complied with these requirements. Pacific Bell should be redirected to differentiate aging numbers between business and residential, track them separately, and report on each category accurately. The CPUC should assess penalties for failure to comply.
6. The Need to Audit the Data
The data analyzed in this utilization study was self-reported by companies. Given the area code crisis in California, the CPUC should audit this data for two reasons. First, verifying number usage data is important to ensure that the public resource of telephone numbers is efficiently managed. Second, audits will help verify whether companies are complying with CPUC and FCC rules for number usage.
Recommendation for Audit
· The CPUC should audit the data submitted by companies in this study and future area code number utilization studies.
CHAPTER THREE: NUMBER POOLING AND OTHER NUMBER CONSERVATION MEASURES
G. INTRODUCTION
Many of the recommendations in Chapter Two resulted directly from the analysis of the utilization data and address actions that the CPUC should undertake to make additional numbers available for either pooling or for the regular monthly lottery. The recommendations contained in this chapter suggest additional conservation measures as required by Public Utilities Code Section 7935(a). The CPUC could adopt the following conservation measures in the 858 area code and statewide: LNP-related actions, Unassigned Number Porting, Rate Center Consolidation, and prefix sharing. When applied, these conservation measures would result in uniform policies which will cause companies to use numbers more efficiently across California and would minimize customer confusion.
H. NUMBER POOLING
Number pooling is an excellent method of number conservation. The CPUC worked aggressively to bring number pooling to California and the results have been dramatic. Pools are underway in nine area codes and five additional pools are scheduled to begin in 2001.
Number pooling has avoided the need to open prefixes and therefore has extended the life of area codes. Prior to pooling, 432 prefixes would have been opened in the 310, 408, 415, 650, 714, 818 and 909 area codes.50 In addition, the pool has satisfied the numbering needs of all companies participating in the pool almost entirely with donated blocks.51
Pooling benefits not only the public but the companies as well by reducing the time necessary to acquire numbering resources. Without pooling, activating new numbers takes at least 66 days.52 With number pooling, activating new numbers can be accomplished in three weeks.
1. More Accurate Forecasting Will Improve Number Pooling
So far in California, number pooling has worked well because companies have met their numbering needs from the excess numbers other companies donate to the pool. The CPUC has set aside prefixes in each area code that will be used to replenish the pools if and when donations are no longer sufficient. There are a limited number of set aside prefixes, so it is crucial that these prefixes be opened only when there is truly a need.
If donated numbers are not sufficient to meet the companies' forecasts, a new prefix may need to be opened. Industry guidelines suggest replenishing a pool at least 66 days in advance when the forecast shows a company will need more numbers than the pool has on hand. This presents a problem, as companies in California have been, on average, forecasting nearly six times more numbers than they will take from the pool. Had the pool administrator opened prefixes based on the forecast, the prefixes would lie unused in the rate center.53
The CPUC has thus far prevented prefixes from being unnecessarily opened by ordering the Pooling Administrator (PA) to consult with TD prior to opening any prefix. However, the CPUC believes this issue should be addressed for the long term. Industry guidelines encourage companies to over-forecast, because a company can only be assured numbers for which it forecasts.54 In essence, a company could be penalized for under-forecasting. Since there is no penalty for over-forecasting, it is in companies' interests to err on the side of over-forecasting. TD recommends the CPUC develop specific rules guiding company forecasting. TD also recommends that the PA take historical usage into account when determining when to open a fresh prefix of 10,000 numbers.
Recommendations for Number Pooling
· The CPUC should work with industry groups and the Pooling Administrator to develop specific rules for companies pertaining to forecasting a six-month inventory when a number pool is authorized in a particular area code.
I. LACK OF LOCAL NUMBER PORTABILITY STANDS AS A KEY BARRIER TO POOLING
Full LNP deployment in the 858 area code is critical to effective number conservation. As described in Chapter 1, LNP enables customers to keep their telephone numbers when they switch companies. Because the number remains with the customer and can be transferred to different companies, there is no need to distribute duplicate numbering resources to both companies. Also, LNP is the technology platform that makes number pooling possible.
In an order released in 1997, the FCC ordered all wireline carriers in the top 100 MSAs to become LNP capable by December 1998.55 The 858 area code falls within one of the top 100 MSAs. The study revealed that all but two wireline carriers in the 858 area code are LNP capable. These companies hold 72,000 numbers that could be made available for number pooling, if they implemented LNP technology.56 On July 26, 2001, the CPUC gave noncompliant carriers an incentive to implement LNP capability by allowing them to receive numbering resources only through the number pool, once a number pool has been established in the area code.57
Wireless carriers, however, requested and received from the FCC an extension of time, until November 2002, to become LNP capable.58 The CPUC filed comments with the FCC arguing that wireless carriers should be required to participate in pooling immediately upon becoming LNP capable. 59 In the Second NRO Report and Order, the FCC agreed with the CPUC and will require wireless carriers to participate in pooling immediately upon becoming LNP capable. Wireless carriers hold 60 prefixes in the 858 area code, of which 312 blocks could be made available for pooling if they were required to participate in the pool.
As noted earlier, federal LNP requirements are directed at companies in the country's top 100 MSAs. But roughly 40% of the area codes in California fall partially or completely outside of these MSAs. These area codes are facing similar numbering crises, and LNP is not ordered. Without full activation of LNP throughout California, the CPUC is effectively prevented from operating number pools in a large portion of the area codes in the state. California has a pending petition at the FCC to extend LNP deployment statewide. The CPUC should urge the FCC to act on the petition for authority to order LNP capability statewide.
Recommendations for LNP
· The CPUC should continue to work with the FCC to enforce LNP capability mandates for all wireline carriers in the top 100 MSAs.
J. UNASSIGNED NUMBER PORTING
Unassigned Number Porting (UNP) is the term used to describe the transfer of unused numbers from one company to another. Like number pooling and the porting of assigned numbers from company to company, UNP is made possible by deployment of LNP. The primary benefit of UNP would be increased access to unused numbers stranded in carrier inventories. UNP would also strengthen competitively neutral access to public numbering resources by enabling companies with smaller inventories to access the inventories of companies with larger number holdings.
UNP would allow companies to transfer small increments of numbers between themselves. Various proposals have suggested limiting the increments to 25 or 100 numbers.60 Two efficiencies would be gained: 1) companies with smaller scale needs would be able to receive numbers in increments appropriate to meet their needs, and 2) unused numbers stranded in company inventories would be transferred to companies where they could be put to use.
Currently, companies receive unused numbers from the NANPA or the PA in increments of 10,000 numbers (prefixes) or 1,000 numbers (blocks). In areas without number pooling, prefixes held in company inventories that are not put to use within six months must be returned, but only if uncontaminated. If just one number has been used, the remaining 9,999 are stranded in the company inventory. In areas with number pooling, blocks are eligible for return only if 10% or less contaminated. For example, if a company receives 1000 numbers and only has need for 100 numbers, the remaining 900 numbers are eligible for return. However, if a company received 1000 numbers and only has need for 101 numbers, the remaining 899 numbers are ineligible for return and are stranded in the company inventory. UNP is one way to address the problem of stranded numbers.
The FCC has contemplated UNP but has so far declined to act.61 The FCC has not ruled out UNP as a conservation measure.62 In the absence of a voluntary company agreement to implement UNP, however, the CPUC could only implement UNP with FCC approval. Given the number conservation benefits to be had, the CPUC should petition the FCC for authority to undertake a UNP trial.
Recommendations for UNP
· The CPUC should petition the FCC for authority to implement UNP statewide.
· The CPUC should solicit comments in order to develop rules and practices necessary to implement UNP.
K. CONSOLIDATION OF RATE CENTERS TO MAXIMIZE NUMBER USE
Rate Center Consolidation (RCC) is a potential number conservation tool because it allows companies to use numbers over a larger geographic area, thus slowing the rate at which prefixes are used. Rate center location dictates both the scope of a customer's local calling area and the charges assessed per toll call. In California, each rate center governs a relatively small, uniform local calling area, measured from the rate center of each exchange. Because the local calling areas in California are small compared to those in many other states, it is virtually impossible to migrate to larger calling areas via consolidation of rate centers without eliminating at least some toll call routes.
Eliminating toll routes would have the residual effect of reducing revenues for toll service providers, which include both local exchange carriers and interexchange carriers. The two major ILECs in California, Pacific Bell and Verizon (formerly GTE California), have expressed at industry meetings their belief that they should be "made whole" for any loss of toll revenues that likely would result from consolidating rate centers. An industry task force which the CPUC charged with developing a proposal for rate center consolidation reported to the CPUC in March 1999 that it would offer no such plan until the CPUC addresses revenue and consumer impact issues. However, it is difficult, if not impossible for the CPUC to address consumer and revenue impacts if the CPUC has no plan before it for consolidating rate centers, which would provide the context and details for assessing such impacts.
California has roughly 750 rate centers, each of which is the approximate center of a 12-mile local calling area. With no input from the industry, the CPUC cannot begin to guess what approach would be most appropriate. For example, California could consolidate from 750 rate centers to 400, or to 200. Each of those possibilities would present different rate "impacts" for both companies and customers. Alternatively, rather than attempting to consolidate rate centers on a statewide basis, the CPUC could consider consolidating rate centers on an area code-by-area code basis. All rate centers in one area code, for example, could be consolidated into one rate center. This would eliminate both the uniform statewide local calling area of 12 miles and uniform statewide rates for each company, thus generating some amount of customer confusion as individuals travel throughout the state for business or social purposes, or relocate their home or business. Further, because companies would lose toll revenues when rate centers are consolidated and local calling areas expanded, the CPUC would need to address the question of which, if any, companies should be allowed to recover those lost revenues, and if so, how.63
Finally, rate center consolidation will mean direct, substantial, and permanent basic rate increases for many customers, unless the ILECs forgo their claim that RCC should be revenue neutral. Economics and Technology, a Boston consulting group, has projected that ".....rate center consolidation in California could result in a per-access-line increase of $5.56 in basic monthly rates for California ILEC customers."64
This may not be an acceptable option, even though California presently has among the lowest local exchange rates in the country. And, if the ILECs continue to press for revenue neutrality, the very process of determining the amount of those revenues, as well as how those monies should be recovered and from what class(es) of customers, would constitute a rate design proceeding of significant scale and scope. Such a proceeding could consume a tremendous amount of CPUC, industry, and consumer representative resources, and take one to two years.65
Nonetheless, because RCC offers the potential for conserving significant quantities of numbers in California, TD recommends that the CPUC renew its efforts to determine how RCC could be implemented in California. The industry should be directed to posit several different scenarios, if they cannot agree on one proposal.
Recommendations for Rate Center Consolidation
· The CPUC should undertake further investigation by ordering the telecommunications industry to develop a plan, within 180 days, for rate center consolidation.
L. SHARING PREFIXES MAY YIELD MORE EFFICIENT NUMBER USE
In analyzing previous utilization data in the 310 area code, TD became aware that two non-affiliated companies were sharing prefixes under an informal arrangement. Using LNP technology, a company with excess numbers had transferred whole thousand-blocks of numbers to the other company for use. TD believes this sharing arrangement promotes efficient number use among companies.
Some companies reporting utilization data in the 760 area code are affiliated through mergers, acquisitions or other business relationships. Despite these affiliations, each company separately requests numbers from the NANPA.66 TD notes that the benefits of sharing prefixes may be different in area codes in which number pooling has already been implemented versus those that number pooling has not been implemented. Sharing prefixes between companies appears worthy of further investigation by the CPUC as a mechanism to promote more efficient use of numbers.
Recommendations for Sharing of Prefixes
· The CPUC should further explore sharing of prefixes as a means to more efficiently utilize numbers in all area codes
CONCLUSION
Analyzing the utilization data provided by carriers has provided useful information regarding number availability and usage practices in the 858 area code. It has also offered insights into developing better public policies to improve efficiency of number use.
We now know that of the approximately 7.7 million usable numbers in the 858 area code, roughly 6.0 million, or approximately three quarters, presently are not in use. Despite the increasing demand for numbers, the 858 area code is not fully utilized. The data indicates that there is considerable room for growth within the existing 858 area code, and it is premature to consider splitting or overlaying the 858 area code at this time.
The CPUC already has directed carriers to employ measures to use the numbering resources in 858 more efficiently. Recently adopted fill rates and sequential numbering rules will insure that carriers better use their existing resources, and receive additional numbers only on an as-needed basis. When pooling takes effect in the 858 area code, all LNP-capable carriers will be given numbers expeditiously and in usable blocks. Allocating numbers in thousand-block increments rather than in full prefixes of 10,000 numbers ensures that the numbering resources are used more efficiently and can greatly extend the life of the existing area code. Implementing these more efficient numbering practices is an important first step, but more needs to be done.
In analyzing the carrier data, it is now clear that because of 1) past inefficiencies in numbering policies and practices, 2) the 10% contamination ceiling for block donations to pooling, and 3) the deferral of LNP capability for wireless carriers, 1.2 million numbers are not in use in 858 but cannot be reassigned to other carriers. Changing contamination thresholds, implementing UNP, and requiring LNP capability for all companies could make some of these stranded numbers available for reassignment.
The CPUC should continue its collaborative process with the FCC and the telecommunications industry to implement Unassigned Number Porting, the development of non-geographic-specific area codes, and other measures which will more fully utilize numbers. The CPUC should begin implementation of the many number conservation and management practices found in the Recommendations Section of this report. As a public resource, it is important that our numbering supplies are used as efficiently and effectively as possible.
APPENDIX A-1
DEFINITIONS FOR UTILIZATION STUDY
Administrative: Administrative numbers are numbers used by telecommunications carriers to perform internal administrative or operational functions necessary to maintain reasonable quality of service standards. Subcategories used in the Utilization Studies are:
· Internal Business Purpose/Official Numbers: A number assigned by a service provider for its own internal business purposes
· Test Numbers: Telephone numbers (TNs) assigned for inter-and intra-network testing purposes
· Other Administrative Numbers (include only Location Routing Number, Temporary Local Directory Number and Wireless E911 ESRD/ESRK) where
· Identical to a Local Routing Number (LRN): The ten-digit (NPA-XXX-XXXX) number assigned to a switch/point of interconnection (POI) used for routing in a permanent local number portability environment
· Temporary Local Directory Number (TLDN): A number dynamically assigned on a per call basis by the serving wireless service provider to a roaming subscriber for the purpose of incoming call setup
· Wireless E-911 ESRD/ESRK: A ten-digit number used for the purpose of routing an E911 call to the appropriate Public Service Answering Point (PSAP) when that call is originating from wireless equipment. The ESRD identifies the cell site and sector of the call origination in a wireless call scenario. The Emergency Services Routing Key (ESRK) uniquely identifies the call in a given cell site/sector and correlates data that is provided to a PSAP by different paths, such as the voice path and the Automatic Location Identification (ALI) data path. Both the ESRD and ESRK define a route to the proper PSAP. The ESRK alone, or the ESRD and/or Mobile Identification Number (MIN), is signaled to the PSAP where it can be used to retrieve from the ALI database, the mobile caller's call-back number, position and the emergency service agencies (e.g., police, fire, medical, etc.) associated with the caller's location. If a NANP telephone number is used as an ESRD or ESRK, this number cannot be assigned to a customer.
For convenience, "other administrative numbers" are reported as a group for purposes of the Utilization Study
Aging Numbers: Aging numbers are disconnected numbers that are not available for assignment to another end user or customer for a specified period of time. Numbers previously assigned to residential customers may be aged for no more than 90 days. Numbers previously assigned to business customers may be aged for no more than 360 days. For purposes of the Utilization Study, carriers are to separately report aging numbers associated with residential service from those associated with business service.
APPENDIX A-1 (continued)
Assigned Numbers: Assigned numbers are numbers working in the Public Switched Telephone Network under an agreement such as a contract or tariff at the request of specific end users or customers for their use, or numbers not yet working but having a customer service order pending. Numbers that are not yet working and have a service order pending for more than five days shall not be classified as assigned numbers. For purposes of the Utilization Studies, numbers for non-working wireless and for interim number portability are to be considered as assigned numbers in Part 1-Section A and separately identified in Part 2. See Interim Number Portability and Non-Working Wireless for definitions.
Available Numbers: Available numbers are numbers that are available for assignment to subscriber access lines, or their equivalents, within a switching entity or point of interconnection and are not classified as assigned, intermediate, administrative, aging, or reserved.
COC Type: Three-digit element defining the use of the Central Office Code (codes such as 0XX used for access tandem and testboard addressing or a "+" symbol that indicates direct routing to the designated switch in the NPA. 2XX-9XX values are considered NXXs.) Allowable codes in the LERG Destination Code by LATA and Tandem Homing Arrangements (LERG 6/9) are:
ATC = Access Tandem Code (0/1XX)
CDA = Customer Directory Assistance only (555 line numbers are assigned by
the North American Numbering Plan Administration)
EOC = End Office Code
PLN = Planned Code - non-routable
PMC = Public Mobile Carrier (Type 2 Interconnected)
RCC = Radio Common Carrier (Dedicated Type 1 Interconnected)
SIC = Special 800 Service Code
SP1 = Service Provider - Miscellaneous Service (Type 1 Interconnected)
SP2 = Service Provider - Miscellaneous Service (Type 2 Interconnected)
TST = Standard Plant Test Code
Allowable codes in the LERG Oddball file (LERG6ODD only) are:
700 = 700 IntraLATA Presubscription
AIN = Advanced Intelligent Network
BLG = Billing Only
BRD = Broadband
CTV = Cable Television
ENP = Emergency Preparedness
FGB = Feature Group B Access
HVL = High Volume
INP = Information Provider
LTC = Local Test Code
N11 = N11 Code
ONA = Open Network Architecture
PRO = Protected
RSV = Reserved
RTG = Routing Only
UFA = Unavailable for Assignment
APPENDIX A-1 (continued)
Interim Number Portability (INP): The interim ability to move telephone service from one service provider to another service provider using Remote Call Forwarding (RCF), Direct Inward Dialing (DID), or equivalent means where:
· Remote Call Forwarding allows a customer to have a local telephone number in a distant location. Every time someone calls that number, that call is forwarded to the RCF customer in the distant location. Remote call forwarding is similar to call forwarding on a residential line, except that the RCF customer has no phone, no office and no physical presence in that location.
· A DID (Direct Inward Dial) trunk is a trunk from the Central office which passes the last two to four digits of the Listed Directory Number into the PBX, thus allowing the PBX to switch the call to and thus ring the correct extension" without the use of an attendant (Newton's Telecom Dictionary). Existing DID retail service is limited to PBX services. For purposes of providing INP, Pacific and GTEC will use the DID switch functionality to provide INP to any CLC customer regardless of the type of terminal equipment used on the customers' premises.
· For the purposes of the Utilization Study, each carrier must report the quantity of its assigned numbers that are dedicated to providing INP under Assigned Numbers in Part 1-Section A and separately identified in Part 2.
Intermediate Numbers: Intermediate numbers are numbers that are made available for use by another telecommunications carrier or non-carrier entity for the purpose of providing telecommunications service to an end user or customer. Numbers ported for the purpose of transferring an established customer's service to another service provider shall not be classified as intermediate numbers. For Type 1 donor carriers, Type 1 numbers are to be reported as intermediate numbers in Part 1-Section A and detailed information is to be provided in Part 2 for the Utilization Studies. For Type 1 recipient donors, Type 1 numbers shall be reported in the Part 1-Section B for the Utilization Studies. For definition, see Type 1 numbers.
Local Number Portability: The ability to move a telephone number from one service provider to another service provider using LRN-LNP technology
APPENDIX A-1 (continued)
Non-Working Wireless: this category is for wireless companies only to report numbers that they have already assigned to customer equipment, but are not yet working. For example, cellular carriers often pre-package a cellular telephone with an assigned telephone number for sale to customers. Those phone numbers are assigned, but are not actually activated until after the customer purchase is made. For the purposes of the Utilization Study, each carrier must report the quantity of its non-working wireless numbers under Assigned Numbers in Part 1-Section A and separately identified in Part 2.
OCN: Operating Company Number (OCN) assignments must uniquely identify the applicant. Relative to CO Code assignments, NECA-assigned Company Codes may be used as OCN's. Companies with no prior CO Code or Company Code assignments should contact NECA (973-884-8355) to be assigned a Company Code(s). Since multiple OCNs and/or Company codes may be associated with a given company, companies with prior assignments should direct questions regarding appropriate OCN usage to the Traffic Routing Administration (TRA) on 732-699-6700
Reserved Numbers: Reserved numbers are numbers that are held by service providers at the request of specific end users or customers for their future use. Numbers held for specific end users or customers for more than 45 days shall not be classified as reserved numbers.
Special Use NXX Codes: Certain NXX codes have traditionally been reserved or designated for special uses, and have not been available for assignment by carriers for general commercial use in providing telephone numbers to customers. These NXX prefixes are restricted to such special uses as recorded public information announcements of time-of-day and weather forecasts, high-volume call-in numbers, and emergency access numbers used by the Federal Emergency Management Administration (FEMA), etc.
Type 1 Numbers: numbers pursuant to a Type 1 interconnection agreement. The Type 1 interconnection is a connection between a mobile/wireless service provider and an end office of another service provider for the purpose of originating and terminating traffic or for access to end user services (i.e. DA, Operator services, 911, etc). The interconnection consists of a facility between the mobile/wireless service provider and the end office, switch usage, and telephone numbers (only required if the mobile carrier wishes to receive originating (L/M) traffic). For the purposes of the 310 Utilization Study, both mobile/wireless service providers who have received Type 1 numbers and those service providers who have provided Type 1 numbers to mobile/wireless service providers are asked to report on those numbers at the 1000 block level.
APPENDIX A | |
TABLE A-2 | |
LIST OF CARRIERS IN THE 858 AREA CODE | |
1 |
AIRTOUCH CELLULAR - CA (VERIZON) |
2 |
AIRTOUCH PAGING - CALIFORNIA (VERIZON MESSAGING) |
3 |
ALLEGIANCE TELECOM, INC.-CA (no disk) |
4 |
ARCH PAGING, INC. |
5 |
AT&T FIXED WIRELESS GROUP |
6 |
AT&T LOCAL |
7 |
BROADBAND OFFICE COMMUNICATIONS, INC. |
8 |
COOK TELECOM, INC. |
9 |
COX CALIFORNIA TELECOM, INC. |
10 |
GLOBAL CROSSING LOCAL SERVICES- CA |
11 |
GST PACIFIC LIGHTWAVE |
12 |
GTE MOBILNET OF CALIFORNIA |
13 |
ICG TELECOM GROUP - CA |
14 |
LEVEL 3 COMMUNICATIONS LLC - CA |
15 |
MAP MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS, INC. |
16 |
MCIMETRO, ATS, INC. |
17 |
MPOWER COMMUNICATIONS CORPORATION-LLC |
18 |
NATIONWIDE PAGING, INC. |
19 |
NET-TEL CORPORATION - CA |
20 |
NETWORK SERVICES LLC |
21 |
NEXTEL COMMUNICATIONS |
22 |
NEXTLINK OF CALIFORNIA (XO) |
23 |
NORTH COUNTY COMMUNICATIONS CORPORATION.-CA |
24 |
O1 COMMUNICATIONS, INC. |
25 |
PACIFIC BELL |
26 |
PACIFIC BELL WIRELESS |
27 |
PACIFIC COAST PAGING, INC. |
28 |
PAC-WEST TELECOMM, INC. |
29 |
PAETEC COMMUNICATIONS, INC. - CA |
30 |
PAGENET |
31 |
PRISM CALIFORNIA OPERATIONS LLC - CA |
32 |
SPRINT COMMUNICATIONS CO, LP-CA |
33 |
SPRINT SPECTRUM LP |
34 |
TELEPORT COMMUNICATIONS GROUP - SAN DIEGO |
35 |
TELIGENT, INC.-CA |
36 |
TIME WARNER COMMUNICATIONS AXS OF CALIFORNIA |
37 |
TSR WIRELESS LLC |
38 |
US TELEPACIFIC CORP - CA |
39 |
WINSTAR WIRELESS, INC.-CA |
40 |
WORLDCOM TECHNOLOGIES, INC.-CA |
Appendix B |
|||||
Table B-1 |
|||||
6.0 Million Available Numbers in the 858 Area Code |
|||||
Wireline Carriers |
1,594,659 |
||||
Wireless Carriers |
372,881 |
||||
Type 1 Carriers |
26,532 |
||||
Subtotal |
1,994,072 |
||||
Available From Code Administration |
2,680,000 |
||||
Set Aside for Pooling |
1,340,000 |
||||
Total |
6,014,072 |
||||
The 2.0 million numbers assigned to carriers are broken down as: |
|||||
Wireline Carriers |
Blocks |
Numbers |
|||
Blocks with 0% contamination (1) |
922 |
922,000 |
|||
Blocks with more than 0% up to 10% |
436 |
420,735 |
|||
Blocks with more than 10% up to 15% |
48 |
42,372 |
|||
Blocks with more than 15% up to 20% |
35 |
28,383 |
|||
Blocks with more than 20% up to 25% |
23 |
18,042 |
|||
Blocks with more than 25% contam. |
1636 |
163,127 |
|||
Total Available Numbers |
1,594,659 |
||||
|
|||||
Wireless Carriers |
|||||
Blocks with 0% contamination (1) |
239 |
239,000 |
|||
Blocks with more than 0% up to 10% |
73 |
71,125 |
|||
Blocks with more than 10% up to 15% |
6 |
5,260 |
|||
Blocks with more than 15% up to 20% |
3 |
2,466 |
|||
Blocks with more than 20% up to 25% |
3 |
2,331 |
|||
Blocks with more than 25% contam. |
276 |
52,699 |
|||
Total Available Numbers |
372,881 |
||||
Type 1 Carriers |
|||||
Reported as Intermediate Numbers by Donors |
76,395 |
||||
Reported as Unavailable Numbers by Type 1 Carriers |
-47,646 |
||||
Est. of Unavailable Numbers of Remaining Type 1 Carriers (2) |
-2,217 |
||||
Total Available Numbers |
26,532 |
||||
(1) Three companies holding nine codes did not submit utilization data. These 90,000 numbers | |||||
have been counted as available in 90 0% contaminated blocks. All three companies are out of | |||||
business as reported to NeuStar. |
|||||
(2) Off the 76,395 numbers reported by donors as Type 1 numbers, Type 1 recipients only | |||||
reported on 72,999 numbers with 47,646 as unavailable and 25,353 as available. |
|||||
Therefore, 3,396 numbers are unaccounted for. Staff estimated the unavailable numbers for | |||||
the unaccounted numbers using the same ratio as numbers that were reported, namely |
|||||
47,646 divided by 72,999. |
|||||
Appendix B | ||
Table B-2 | ||
Numbers Potentially Available Under Different Pooling Scenarios | ||
Running Total | ||
Wireline Carriers: Current Level at 10% or less (1) |
789,225 |
|
Set Aside for Pooling |
1,340,000 |
|
Available from Code Administration |
2,680,000 |
|
Subtotal |
4,809,225 |
4,809,225 |
Other Possibilities for Pooling: |
||
Available Numbers for non LNP blocks of Wireline Carriers |
80,985 |
4,890,210 |
Unavailable Numbers from Special Use Codes (2) |
20,000 |
4,910,210 |
Wireline Carriers: Up to 15% |
42,372 |
4,952,582 |
Wireline Carriers: Up to 20% |
28,383 |
4,980,965 |
Wireline Carriers: Up to 25% |
18,042 |
4,999,007 |
Cellular and PCS Carriers: Up to 10% (3) |
153,024 |
5,152,031 |
Cellular and PCS Carriers: Up to 15% (3) |
2,595 |
5,154,626 |
Cellular and PCS Carriers: Up to 20% (3) |
1,217 |
5,155,843 |
Cellular and PCS Carriers: Up to 25% (3) |
1,150 |
5,156,993 |
Type 1 Carriers: Up to 10% |
0 |
5,156,993 |
Type 1 Carriers: Up to 15% |
0 |
5,156,993 |
Type 1 Carriers: Up to 20% |
1,662 |
5,158,655 |
Type 1 Carriers: Up to 25% |
0 |
5,158,655 |
Paging Carriers: Up to 10% (3) |
157,101 |
5,315,756 |
Paging Carriers: Up to 15% (3) |
2,665 |
5,318,421 |
Paging Carriers: Up to 20% (3) |
1,249 |
5,319,670 |
Paging Carriers: Up to 25% (3) |
1,181 |
5,320,851 |
Total |
5,320,851 |
|
(1) Actual numbers available to the pool after carriers keep the allowed six-month inventory | ||
were estimated from the 1,261,750 available numbers in LNP-capable, non-special-use | ||
blocks that are 10% or less contaminated, using the ratio of pooling donations to total | ||
10% or less contaminated blocks (62.55%) from the 310 pool. |
||
(2) See discussion on special use codes in Section D.1.c. |
||
(3) While cellular and PCS carriers have until November 2002 to become LNP capable, | ||
paging companies currently are totally exempted. Therefore, TD calculated the available | ||
numbers held by paging carriers versus cellular/pcs carriers and applied that percentage | ||
to the total wireless available numbers in the different contamination levels. | ||
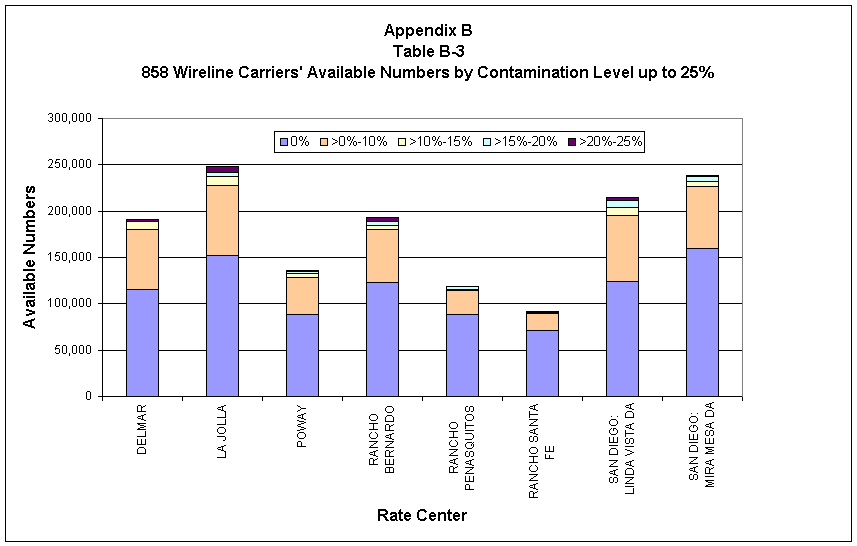
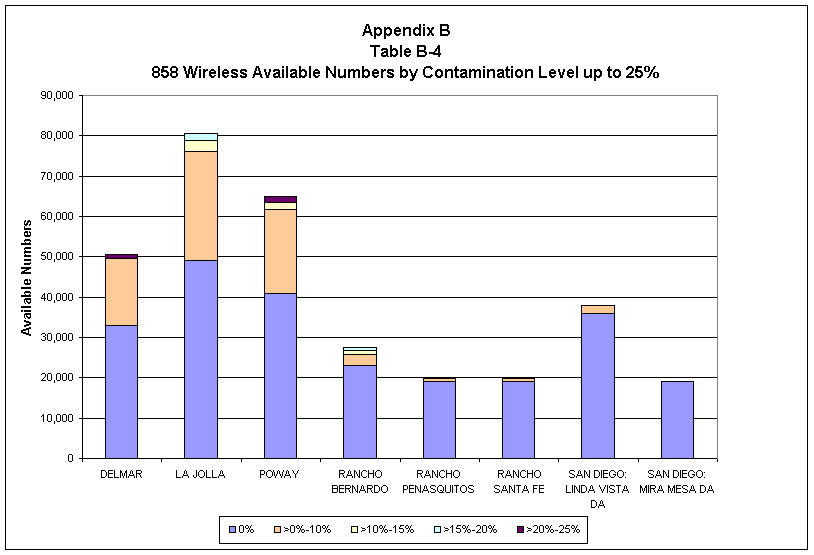

APPENDIX C | ||
|
| |
858 SPECIAL USE CODES | ||
|
| |
NXX |
PURPOSE |
UNAVAILABLE |
|
| |
289 |
Weather Service |
10000 |
555 |
Customer Directory Assistance |
10000 |
570 |
High Volume Calling |
10000 |
853 |
Time Service |
10000 |
Appendix D-1 | |||||
Wireline Reserved Numbers | |||||
Number of |
Numbers |
||||
Wireline |
Assigned to |
Reserved | |||
Rate Center |
Carriers |
|
Wireline |
|
Numbers |
DELMAR |
21 |
110,833 |
7,770 | ||
LA JOLLA |
24 |
480,066 |
33,239 | ||
POWAY |
15 |
58,040 |
5,690 | ||
RANCHO BERNARDO |
20 |
140,020 |
7,625 | ||
RANCHO PENASQUITOS |
13 |
41,313 |
638 | ||
RANCHO SANTA FE |
10 |
10,926 |
597 | ||
SAN DIEGO: LINDA VISTA DA |
21 |
232,437 |
16,613 | ||
SAN DIEGO: MIRA MESA DA |
24 |
165,395 |
8,083 | ||
858 NPA DA |
1 |
|
0 |
|
0 |
TOTALS |
1,239,030 |
80,255 | |||
Appendix D-2 | |||||
Wireless Reserved Numbers | |||||
Number of |
Numbers |
||||
Wireless |
Assigned to |
Reserved | |||
Rate Center |
Carriers |
|
Wireless |
|
Numbers |
DELMAR |
4 |
4,089 |
1 | ||
LA JOLLA |
8 |
70,166 |
6,022 | ||
POWAY |
5 |
72,371 |
153 | ||
RANCHO BERNARDO |
4 |
8,440 |
3,000 | ||
RANCHO PENASQUITOS |
2 |
7,184 |
0 | ||
RANCHO SANTA FE |
2 |
0 |
0 | ||
SAN DIEGO: LINDA VISTA DA |
6 |
16,057 |
3,013 | ||
SAN DIEGO: MIRA MESA DA |
2 |
613 |
0 | ||
858 NPA DA |
0 |
|
0 |
|
0 |
TOTALS |
178,920 |
12,189 | |||
Appendix E-1 | |||||||||||
Wireline Administrative Numbers | |||||||||||
Number of |
Numbers |
Employee/ |
|||||||||
Wireline |
Assigned to |
Official |
Total Admin | ||||||||
Rate Center |
Carriers |
|
Wireline |
|
Numbers |
|
Test |
|
Other |
|
Numbers |
DELMAR |
21 |
110,833 |
624 |
721 |
210 |
1,555 | |||||
LA JOLLA |
24 |
480,066 |
3,296 |
1,047 |
211 |
4,554 | |||||
POWAY |
15 |
58,040 |
472 |
783 |
5 |
1,260 | |||||
RANCHO BERNARDO |
20 |
140,020 |
594 |
639 |
206 |
1,439 | |||||
RANCHO PENASQUITOS |
13 |
41,313 |
583 |
709 |
1 |
1,293 | |||||
RANCHO SANTA FE |
10 |
10,926 |
201 |
431 |
1 |
633 | |||||
SAN DIEGO: LINDA VISTA DA |
21 |
232,437 |
25,068 |
926 |
10 |
26,004 | |||||
SAN DIEGO: MIRA MESA DA |
24 |
165,395 |
3,248 |
818 |
10 |
4,076 | |||||
858 NPA DA |
1 |
|
0 |
|
10,000 |
|
0 |
|
0 |
|
10,000 |
TOTALS |
1,239,030 |
44,086 |
6,074 |
654 |
50,814 | ||||||
Appendix E-2 | |||||||||||
Wireless Administrative Numbers | |||||||||||
Number of |
Numbers |
Employee/ |
|||||||||
Wireless |
Assigned to |
Official |
Total Admin | ||||||||
Rate Center |
Carriers |
|
Wireless |
|
Numbers |
|
Test |
|
Other |
|
Numbers |
DELMAR |
4 |
4,089 |
306 |
189 |
460 |
955 | |||||
LA JOLLA |
8 |
70,166 |
409 |
42 |
1,919 |
2,370 | |||||
POWAY |
5 |
72,371 |
300 |
3,764 |
689 |
4,753 | |||||
RANCHO BERNARDO |
4 |
8,440 |
28 |
28 | |||||||
RANCHO PENASQUITOS |
2 |
7,184 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
2 | |||||
RANCHO SANTA FE |
2 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
2 | |||||
SAN DIEGO: LINDA VISTA DA |
6 |
16,057 |
106 |
269 |
1 |
376 | |||||
SAN DIEGO: MIRA MESA DA |
2 |
613 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 | |||||
858 NPA DA |
0 |
|
0 |
|
0 |
|
0 |
|
0 |
|
0 |
TOTALS |
178,920 |
1,121 |
4,296 |
3,069 |
8,486 | ||||||
Appendix F-1 | |||||
Wireline Intermediate Numbers | |||||
Number of |
Numbers |
||||
Wireline |
Assigned to |
Intermediate | |||
Rate Center |
Carriers |
|
Wireline |
|
Numbers |
DELMAR |
21 |
110,833 |
0 | ||
LA JOLLA |
24 |
480,066 |
100 | ||
POWAY |
15 |
58,040 |
0 | ||
RANCHO BERNARDO |
20 |
140,020 |
6,600 | ||
RANCHO PENASQUITOS |
13 |
41,313 |
0 | ||
RANCHO SANTA FE |
10 |
10,926 |
0 | ||
SAN DIEGO: LINDA VISTA DA |
21 |
232,437 |
56,301 | ||
SAN DIEGO: MIRA MESA DA |
24 |
165,395 |
7,500 | ||
858 NPA DA |
1 |
|
0 |
|
0 |
TOTALS |
1,239,030 |
70,501 | |||
Appendix F-2 | |||||
Wireless Intermediate Numbers | |||||
Number of |
Numbers |
||||
Wireless |
Assigned to |
Intermediate | |||
Rate Center |
Carriers |
|
Wireless |
|
Numbers |
DELMAR |
4 |
4,089 |
1,150 | ||
LA JOLLA |
8 |
70,166 |
3,057 | ||
POWAY |
5 |
72,371 |
6,139 | ||
RANCHO BERNARDO |
4 |
8,440 |
2,622 | ||
RANCHO PENASQUITOS |
2 |
7,184 |
1,338 | ||
RANCHO SANTA FE |
2 |
0 |
98 | ||
SAN DIEGO: LINDA VISTA DA |
6 |
16,057 |
97 | ||
SAN DIEGO: MIRA MESA DA |
2 |
613 |
142 | ||
858 NPA DA |
0 |
|
0 |
|
0 |
TOTALS |
178,920 |
14,643 | |||
APPENDIX G | |||
|
| ||
AGING NUMBERS IN THE 858 AREA CODE | |||
|
| ||
|
WIRELESS |
WIRELINE |
TOTAL |
RESIDENTIAL |
11,476 |
49,959 |
61,435 |
BUSINESS |
1,405 |
14,782 |
16,187 |
TOTAL NUMBERS |
12,881 |
64,741 |
77,622 |
APPENDIX H
Summary of Recommendations
Recommendation from Block Contamination Analysis of Wireline Carriers
· The CPUC should petition the FCC to increase the contamination level for pooling to 25%. If the FCC grants the petition, the CPUC should increase the maximum contamination level of donated blocks from 10% to 25% for all LNP-capable carriers.
Recommendations from Block Contamination Analysis of Wireless Carriers
· When cellular and PCS companies become LNP capable in November 2002, the CPUC should direct those wireless carriers to donate to and participate in all number pools in California, using the same contamination threshold for donated blocks in effect for all LNP-capable companies.
· The CPUC staff should meet with paging companies to explore options for consolidating numbering resources in fewer rate centers, as well as other methods of reducing the number of stranded numbers held by paging companies.
Recommendations for Block Contamination Issues Affecting All Carriers
· The CPUC should monitor compliance with its fill rate and sequential numbering policies through future number utilization filings and audits.
*1 The CPUC should establish penalties for non-compliance with fill rate and sequential numbering policies adopted in Decision 00-07-052.67
Recommendations for Treatment of Non-Working Wireless
· Non-working wireless numbers should be treated as reserved numbers and limited to 180 days, after which they should be classified as available for assignment to customers.
· The CPUC should continue to monitor non-working wireless numbers in the near term by reviewing future utilization filings, and should include this category of numbers in any audits conducted of wireless carrier number use.
Recommendations for INP-Related Conservation Measures
· The CPUC should require companies to transition from INP to LNP in the 858 area code and implement a monitoring mechanism to ensure compliance.
· The CPUC should adopt a schedule for transitioning INP arrangements to LNP in all other California area codes.
Recommendations for Special-Use Prefixes
· TD recommends that the CPUC initiate an investigation into the possibility of moving the numbers for time and emergency preparedness into the 555 prefix.
· TD recommends that the CPUC include in its investigation the broader use of the 555 prefix in California's area codes by providing standard 555 numbers in every California area code to provide time, emergency preparedness, and weather information.
Recommendations for Reserved Numbers
· The CPUC should monitor reserved number use for all companies by reviewing future utilization data to ensure companies are complying with the FCC's 180-day requirement.
Recommendation for Intermediate Numbers
· The CPUC should monitor intermediate number use for all companies by reviewing future utilization filings to test whether potential abuses in this reporting category occur.
Recommendations for Type 1 numbers:
· Wireline and wireless carriers should improve Type 1 number inventory management. Wireline carriers should perform a one-time inventory check of wireless Type 1 numbers to verify their records match that of the wireless Type 1 carriers' records. Companies should make inventory data available to the CPUC upon request. Wireline carriers should recover and add to their inventories any Type 1 numbers lying dormant.
· Type 1 carriers should be subject to number conservation techniques such as sequential numbering and fill rates. A system to ensure compliance with Type 1 number conservation measures should be developed.
· The Commission should consider Type 1 numbers as potential donations to the number pool. Excess and unused Type 1 numbers should be returned to the wireline carriers and either used to serve customers or donated to the number pool.
Recommendation for Aging Numbers
· Although the CPUC has required all companies to differentiate aging numbers between residential and business and track the two categories separately, Pacific Bell has not complied with these requirements. Pacific Bell should be redirected to differentiate aging numbers between business and residential, track them separately, and report on each category accurately. The CPUC should assess penalties for failure to comply.
Recommendation for Audit
· The CPUC should audit the data submitted by companies in this study and future area code number utilization studies.
Recommendations for Number Pooling
· The CPUC should work with industry groups and the Pooling Administrator to develop specific rules for companies pertaining to forecasting a six-month inventory when a number pool is authorized in a particular area code.
Recommendations for LNP
· The CPUC should continue to work with the FCC to enforce LNP capability mandates for all wireline carriers in the top 100 MSAs.
Recommendations for UNP
· The CPUC should petition the FCC for authority to implement UNP statewide.
· The CPUC should solicit comments in order to develop rules and practices necessary to implement UNP.
Recommendations for Rate Center Consolidation
· The CPUC should undertake further investigation by ordering the telecommunications industry to develop a plan, within 180 days, for rate center consolidation.
Recommendations for Sharing of Prefixes
· The CPUC should further explore sharing of prefixes as a means to more efficiently utilize numbers in all area codes
11 Another 134 prefixes have been set aside for the future 858 number pool. Also, TD's analysis of available numbers in the remainder of this report uses 268 prefixes available from Code Administration as of the utilization data date of December 31, 2000.
12 See Chapter Three of this report for a discussion of LNP. 13 FCC's Opinion and Order on Telephone Number Portability FCC 97-74, issued March 6, 1997 14 Cellular companies, PCS companies, and paging companies comprise the wireless category. 15 ILECs and CLECs 16 The 858 area code is not in rationing. See Section B1 of Chapter 1.17 The CPUC revised the imminent exhaust criterion from three months to six months in Joint Assigned Commissioner and Administrative Law Judge's Ruling Implementing Revised Procedures to Conform to FCC Order, dated April 30, 2001.
18 Report and Order and Further Notice of Proposed Rulemaking, CC Docket No. 99-200 FCC 00-104 (released March 31, 2000). 19 Wireline carriers include ILECs and CLECs. 20 A further breakdown of the 2.0 million available numbers held by carriers is shown in Appendix B, Table B-1. 21 Type 1 carriers are not considered wireline or wireless companies. Type 1 numbers are programmed in the wireline company's end office, but are used by a wireless company. For further description of Type 1 carriers, see Section D.4.a. 22 4.8 million numbers are comprised of 789,000 estimated pooling donations by companies plus 1.3 million set aside for the future 858 number pool plus 2.7 million available from Code Administration. 23 The recommendations include receiving authority from the FCC to increase contamination threshold (25%) for pooling, recovering blocks from special-use prefixes, recovering unused numbers from non-LNP-capable carriers and Type 1 carriers, and requiring wireless carriers to participate in pooling, as described later in this report. 24 See Appendix B, Table B-2 for a detailed breakout of the 5.3 million numbers. 25 Although all wireline carriers are required to be LNP capable in rate centers within the top 100 MSAs, five wireline carriers in the 858 area code remain non-LNP capable in one or more of the 60 rate centers in the 858 area code that are located within one of the top 100 MSAs. 26 10% or less contaminated means that out of 1,000 numbers in a block, 100 numbers or fewer have been classified as unavailable. 27 Future need may include serving new customers or offering new services. 28 See Chapter 3 for the status of pooling in the 858 area code. 29 See Footnote on Table B-2 in Appendix B for the derivation of this estimate. 30 See Table B-1 in Appendix B. These 252,000 are comprised of 42,372 numbers from blocks that are 10-15% contaminated, 28,383 from 15-20% contaminated, 18,042 from 20-25% contaminated, and 163,127 numbers from blocks that are more than 25% contaminated. Later in this chapter, TD recommends additional steps that can be implemented to make more of these 252,000 numbers available for number pooling. 31 INC's Thousand Block (NXX-X) Pooling Administration Guidelines, dated January 10, 2000, state that carriers should donate specified thousand-blocks. 32 Additional numbers from the last three columns of Table 2-4: 36,093 + 28,383 + 18,042 = 82,518. 33 See footnote 3 of Table B-2, Appendix B, for the derivation of this estimate. 34 See Chapter 1 for the discussion of Decision 00-07-052. 35 This includes the nine prefixes held by the three companies who are out of business in California. 36 FCC 00-104, Paragraphs 237, 238, and 241 37 Remote Call Forwarding allows a customer to have a local telephone number in a distant location. RFC is similar to call forwarding on a residential line, except that the RCF customer has no phone, no office and no physical presence in that location. Direct Inward Dialing uses a trunk from the central office which passes the last two to four digits of the Listed Directory Number into the PBX, thus allowing the PBX to switch the call to the correct extension without the use of an attendant. Existing DID retail service is limited to PBX services. For purposes of providing INP, DID switch functionality is used to provide INP to any CLC customer regardless of the type of terminal equipment used on the customer's premises. 38 The emergency preparedness prefixes are for services other than 911. 39 The number used for inter-area code directory assistance, which is uniform throughout California, is 1-XXX- 555-1212. This number has been designated for this use at the federal level. 40 An example would be a customer request for 2,500 numbers to be used in 2000, coupled with a request to have the next 2,500 numbers in sequence "reserved" for the customer to use in 2001. 41 Central Office Code (NXX) Assignment Guidelines, prepared by the Industry Numbering Committee, January 27, 1999 version, Section 4.4. 42 FCC Order 00-280, CC Docket No. 99-200, adopted and released on July 31, 2000. 43 See FCC Order 00-129, Paragraph 114 44 See Appendix D for a breakdown of reserved numbers reported in the 858 NPA by rate center. 45 See Appendix F for a breakdown of intermediate numbers held by wireline and wireless carriers. 46 Type 1 numbers are programmed in the wireline carrier's end office, but are used by a wireless carrier. 47 46,795 out of a total of 76,395 Type 1 numbers are unaccounted for or mismatched. 48 Type 1 numbers given to wireless carriers are from prefixes in which LNP has already been initiated by the wireline carriers. Because Type 1 numbers reside in the wireline carrier's end office, Type 1 numbers are LNP-capable and thus suited for pooling. 49 In the first NRO Order, both 360 days and 365 days were used as the time period for aging business numbers. In a clarifying order, the FCC adopted 365 days as the aging period for business numbers. When the CPUC sent out the parameters for utilization data for this study, the 360 day time period for aging business numbers was used. In order to be consistent with the time frames the FCC adopted, the CPUC is now using the 365 time period for aging business numbers. 50 As of July 3, 2001. 51 One prefix was opened in the 310 area code to supply numbers to the pool, and two prefixes were opened in the 909 area code to supply numbers to the pool. Several prefixes have been opened for LRN purposes. 52 Before a whole prefix is activated, the prefix must be first listed for 66 days in the Local Exhange Routing Guide (LERG), stating the rate center where the prefix will be located. 53 Data can be found in Pooling Appendix. 54 Sections 6.1.4 & 6.1.5 in INC 99-0127-023, January 10, 2000 55 FCC 96-286 in CC Docket No. 95-116. 56 Two other companies lack LNP capability in some switches in the 858 area code. If these switches were LNP capable, 9,000 additional numbers would be eligible for pooling. 57 CPUC Joint Assigned Commissioner's and Administrative Law Judge's Ruling Regarding Lottery Eligibility and Number Pooling Requirements on July 26, 2001. 58 FCC 99-19, WT Docket 98-229; CC Docket No. 95-116, Released: February 9, 1999. Paging companies are indefinitely exempt from becoming LNP-capable. 59 Further Comments of the California Public Utilities Commission and the People of the State of California in CC Docket No. 99-200, submitted May 19, 2000. 60 See INC Contribution #336R of September 29, 2000, "UNP Architecture With Minimal Administrative Structure" and Focal and MCIWorldcom's Report on UNP Trial 61 NRO Order, FCC 00-104, CC Docket 99-200, ¶ 230. "We reiterate our finding that UNP and ITN [individual telephone number pooling] are not yet sufficiently developed for adoption as nationwide numbering resource optimization measures and conclude that ITN and UNP should not be mandated at this time.". 62 See ¶ 231: "We permit carriers, however, to engage voluntarily in UNP where it is mutually agreeable and where no public safety or network reliability concerns have been identified." 63 For example, while the ILECs still control roughly 95% of the residential toll market, competitors have succeeded in making significant inroads into the business toll market, where the ILECs now hold only 50% of the market. If the CPUC were to decide that the ILECs should be "made whole" for any lost toll revenues, then other companies legitimately could demand a mechanism to make them whole as well. Alternatively, if the competitors cannot practically be reimbursed for lost revenues, then as a policy matter, the CPUC must decide if it is reasonable to allow only the ILECs to recover such revenue.64 "Where Have All the Numbers Gone?" (Second Edition), The Ad Hoc Telecommunications Users Committee, prepared by Economics and Technology, Inc., June 2000. The estimate of $5.56 may be conservative.
65 The last major rate design proceeding undertaken for Pacific Bell and Verizon, then GTEC, was the Implementation and Rate Design (IRD) phase of the New Regulatory Framework proceeding, I.87-ll-033. The IRD phase took three years to complete. 66 Prior to the opening of a number pool, all companies requesting telephone numbers get prefixes from the NANPA. With pooling, only non-LNP-capable carriers receive prefixes from the NANPA, while LNP-capable carriers receive thousand-number blocks from the pooling administrator. 67 See Chapter 1 for the discussion of Decision 00-07-052.